
Chapter 17 - Human resource policies & practices
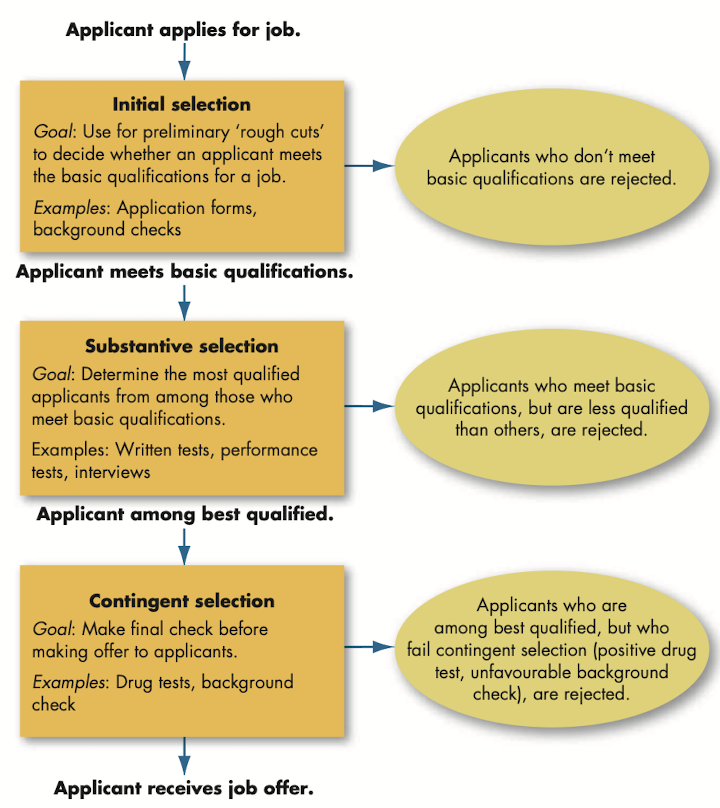
Selection practices
Training and development programs
Four general skill categories
Basic literacy
Technical skills
Inter-personal skills
Problem-solving skills
Training methods
Formal training
Informal training
On-the-job training: job rotation, apprenticeships, understudy assignments and formal mentoring programs.
Off-the-job training: activities such as live classroom lectures, public seminars, self-study programs, Internet courses, webinars, podcasts and group activities that use role-plays and case studies.
Performance evaluation
Three types of behavior that constitute performance at work
Task performance: combination of effectiveness and efficiency at doing your core job tasks.
Citizenship: actions that contribute to the psychological environment of the organization, such as helping others when not required.
Counter-productivity: actions that actively damage the organization, including stealing, behaving aggressively towards co-workers, or being late or absent.
Methods of performance evaluation
Written essays
Critical incidents: way of evaluating the behaviors that are key in making the difference between executing a job effectively and executing it ineffectively.
Graphic rating scales: evaluation method in which the evaluator rates performance factors on an incremental scale.
Behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS): scales that combine major elements from the critical incident and graphic rating scale approaches: the appraiser rates the employees based on items along a continuum, but the points are examples of actual behavior on the given job rather than general descriptions or traits.
Forced comparison: method of performance evaluation where an employee’s performance is made in explicit comparison to others (e.g., an employee may rank third out of ten employees in her work unit).
Group order ranking: evaluation method that places employees into a particular classification, such as quartiles.
Individual ranking: evaluation method that rank-orders employees from best to worst.
Chapter 17 - Human resource policies & practices
Selection practices

Training and development programs
Four general skill categories
Basic literacy
Technical skills
Inter-personal skills
Problem-solving skills
Training methods
Formal training
Informal training
On-the-job training: job rotation, apprenticeships, understudy assignments and formal mentoring programs.
Off-the-job training: activities such as live classroom lectures, public seminars, self-study programs, Internet courses, webinars, podcasts and group activities that use role-plays and case studies.
Performance evaluation
Three types of behavior that constitute performance at work
Task performance: combination of effectiveness and efficiency at doing your core job tasks.
Citizenship: actions that contribute to the psychological environment of the organization, such as helping others when not required.
Counter-productivity: actions that actively damage the organization, including stealing, behaving aggressively towards co-workers, or being late or absent.
Methods of performance evaluation
Written essays
Critical incidents: way of evaluating the behaviors that are key in making the difference between executing a job effectively and executing it ineffectively.
Graphic rating scales: evaluation method in which the evaluator rates performance factors on an incremental scale.
Behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS): scales that combine major elements from the critical incident and graphic rating scale approaches: the appraiser rates the employees based on items along a continuum, but the points are examples of actual behavior on the given job rather than general descriptions or traits.
Forced comparison: method of performance evaluation where an employee’s performance is made in explicit comparison to others (e.g., an employee may rank third out of ten employees in her work unit).
Group order ranking: evaluation method that places employees into a particular classification, such as quartiles.
Individual ranking: evaluation method that rank-orders employees from best to worst.
 Knowt
Knowt
