
4.1 Types of Chemical Bonds
Electrostatic forces that hold atoms together in compounds
Involves the interaction of the valance electrons
Ionic Chemical Bonds
electrons and transferred between oppositely charged ions
form ionic compounds with ionic bonding
ions form to become isoelectronic with a noble gas, same electron configuration
Isoelectronic: same electron configuration as another
Covalent Chemical Bonds
electrons are shared
forms molecular compounds
Nonpolar, polar or pure
Molecular element: pure substance made up of 2 atoms like Oxygen
As two atoms move close together, the electron cloud of one attracts the nucleus of the other
At the same time the nuclei repel each other as do the electron cloud
The atoms stay a distance from one another that has the lowest overall energy of the system like the hydrogen molecule.
Inter: how the molecules are attracting with one another like London Dispersion, Hydrogen Bonding & Dipole-Dipole
Intra: what is holding the molecule togehter like Covalent or Ionic
Lewis Theory of Bonding
Atoms & ions are stable if they have a full valence shell of electrons
Electrons are most stable when they are paired
Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full valence shell of electrons
A full valence shell of electrons may be achieved by an exchange of electrons between metal and non-metal atoms
The sharing of electrons results in a covalent bond
Duet / Octet Rule
Hydrogen is stable with 2 electrons
Most atoms are stable with 8 electrons
Lewis Structures
Draw the central atom (highest bonding capacity)
Arrange the symbols of the atoms for the rest of the elements around equal distance apart
Add up the number of valence electrons of each atom. Add to this any negative charge or subtract any positive charge.
Place a pair of bonded electrons between central atom and each of the others (single bond).
Place lone electron pairs on outer atoms first (follow duet and octet rule)
Dump rest of electrons on central atom in pairs
Move electrons around to form double or triple bonds until all atoms follow octet/duet rule.
Resonance Structures: models that give the relative position of atoms in a Lewis Structure, but show different places for their bonding and lone pairs
Exceptions
Under filled octets: molecules who’s central atoms are surrounded by fewer than 8 electrons
Ex: Boron Trifluoride
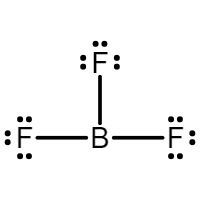
Overfilled octets: molecules whose central atoms are surrounded by more than 8 electrons
Sulfur has its valence electrons in the third energy level
There is space for 12 electrons in the valence shells
Sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine
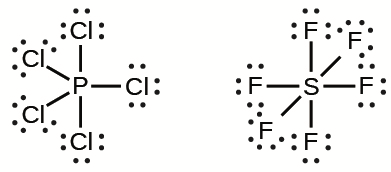
Determining Formal Charge
Formal charge of a molecule to determine its most stable structure
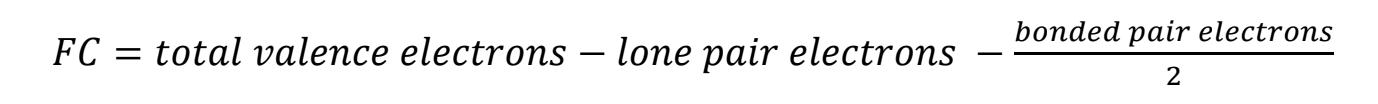
Determine for each atom, then add all atoms together to determine charge of molecule
The arrangement with which charges are the most stable
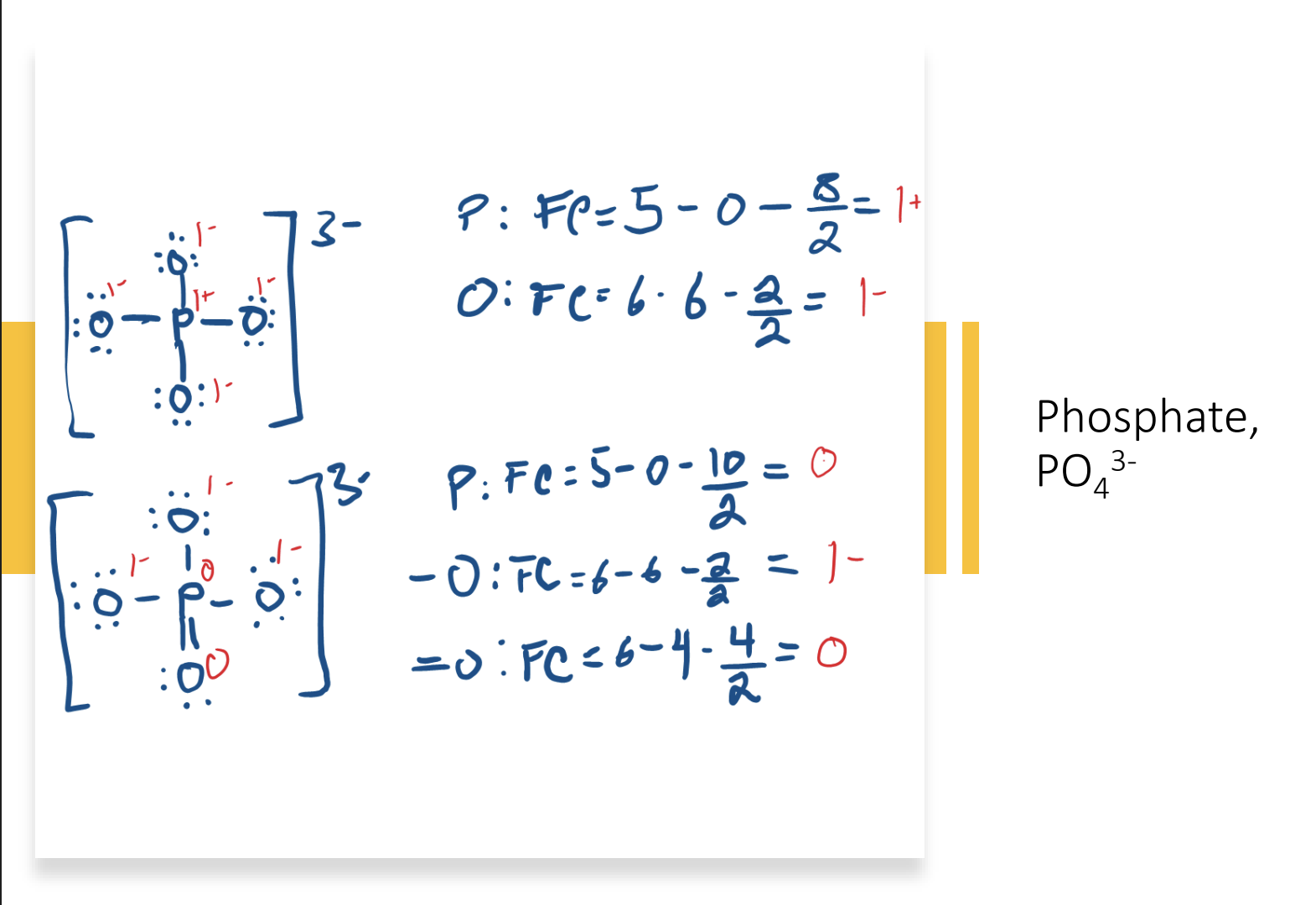
The arrangement where P has an overfilled octet contains fewer charges than the arrangement where P has a normal octet
Certain elements are able to do this because they have an empty 3d orbital that electrons can fill
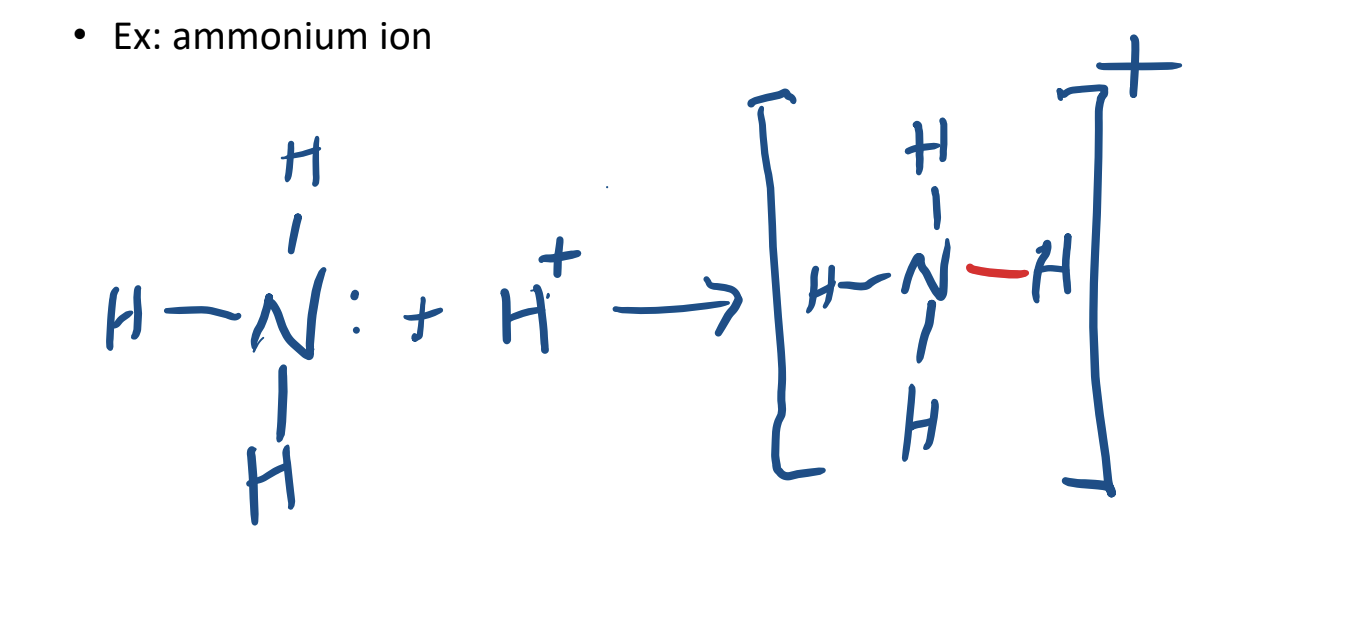
Coordinate Covalent Bonding
a covalent bond in which the both of the bonding electrons are from one atom
4.1 Types of Chemical Bonds
Electrostatic forces that hold atoms together in compounds
Involves the interaction of the valance electrons
Ionic Chemical Bonds
electrons and transferred between oppositely charged ions
form ionic compounds with ionic bonding
ions form to become isoelectronic with a noble gas, same electron configuration
Isoelectronic: same electron configuration as another
Covalent Chemical Bonds
electrons are shared
forms molecular compounds
Nonpolar, polar or pure
Molecular element: pure substance made up of 2 atoms like Oxygen
As two atoms move close together, the electron cloud of one attracts the nucleus of the other
At the same time the nuclei repel each other as do the electron cloud
The atoms stay a distance from one another that has the lowest overall energy of the system like the hydrogen molecule.
Inter: how the molecules are attracting with one another like London Dispersion, Hydrogen Bonding & Dipole-Dipole
Intra: what is holding the molecule togehter like Covalent or Ionic
Lewis Theory of Bonding
Atoms & ions are stable if they have a full valence shell of electrons
Electrons are most stable when they are paired
Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full valence shell of electrons
A full valence shell of electrons may be achieved by an exchange of electrons between metal and non-metal atoms
The sharing of electrons results in a covalent bond
Duet / Octet Rule
Hydrogen is stable with 2 electrons
Most atoms are stable with 8 electrons
Lewis Structures
Draw the central atom (highest bonding capacity)
Arrange the symbols of the atoms for the rest of the elements around equal distance apart
Add up the number of valence electrons of each atom. Add to this any negative charge or subtract any positive charge.
Place a pair of bonded electrons between central atom and each of the others (single bond).
Place lone electron pairs on outer atoms first (follow duet and octet rule)
Dump rest of electrons on central atom in pairs
Move electrons around to form double or triple bonds until all atoms follow octet/duet rule.
Resonance Structures: models that give the relative position of atoms in a Lewis Structure, but show different places for their bonding and lone pairs
Exceptions
Under filled octets: molecules who’s central atoms are surrounded by fewer than 8 electrons
Ex: Boron Trifluoride

Overfilled octets: molecules whose central atoms are surrounded by more than 8 electrons
Sulfur has its valence electrons in the third energy level
There is space for 12 electrons in the valence shells
Sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine
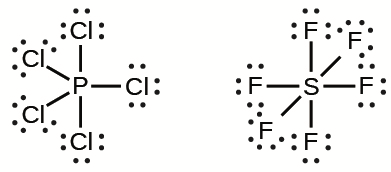
Determining Formal Charge
Formal charge of a molecule to determine its most stable structure
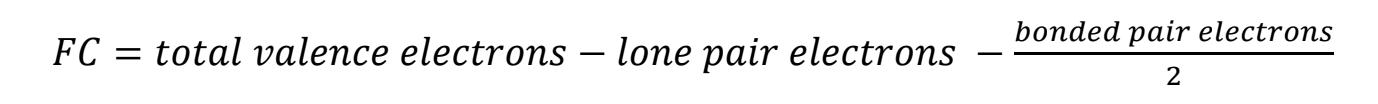
Determine for each atom, then add all atoms together to determine charge of molecule
The arrangement with which charges are the most stable

The arrangement where P has an overfilled octet contains fewer charges than the arrangement where P has a normal octet
Certain elements are able to do this because they have an empty 3d orbital that electrons can fill
Coordinate Covalent Bonding
a covalent bond in which the both of the bonding electrons are from one atom

 Knowt
Knowt
