
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomy: The study of the body's structures and the relationship of its parts to each other.
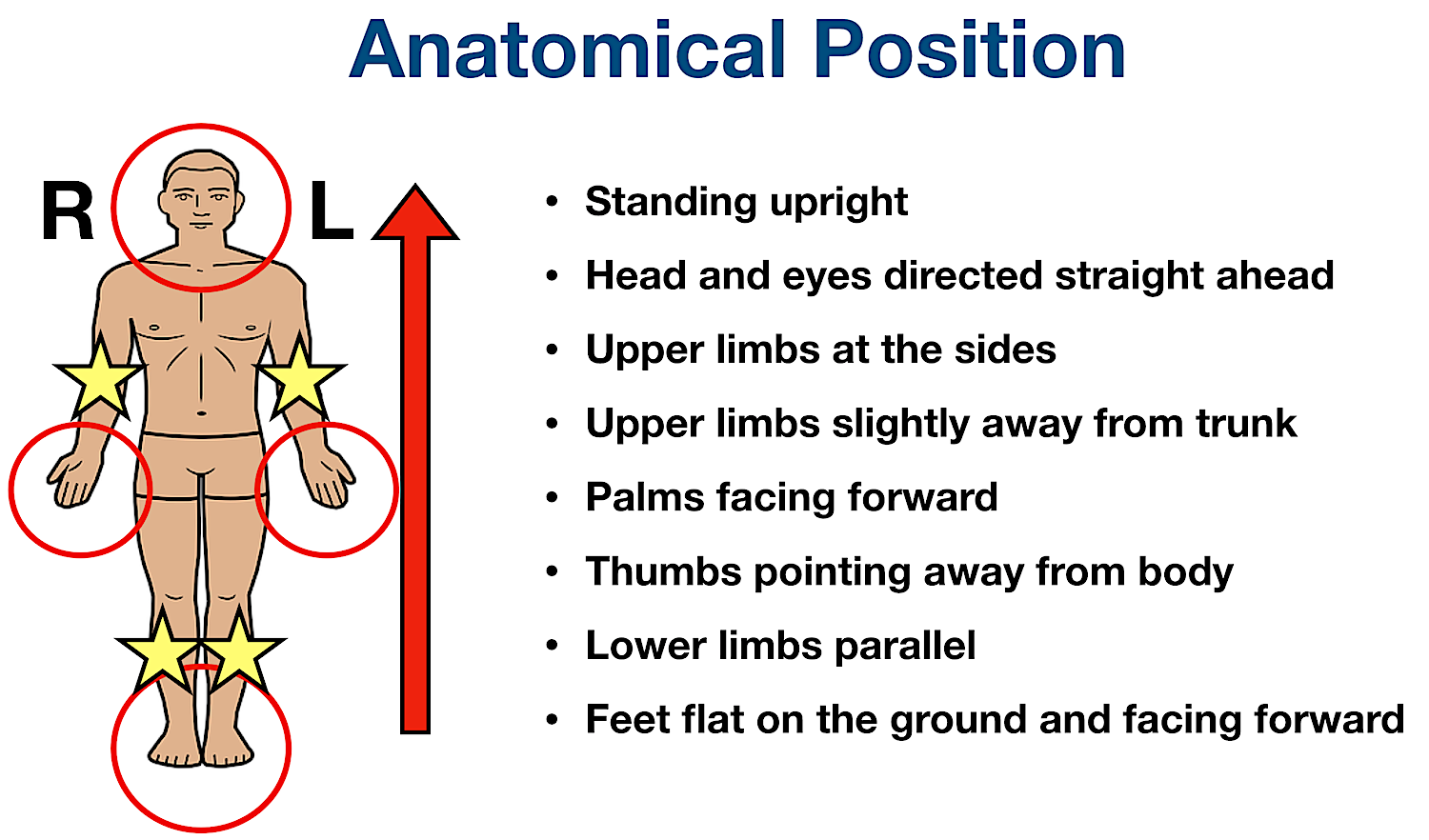
Anatomical Position
the anatomical position is the standard reference position of the body
the body is in an erect posture
the face and the palms are facing forward
the feet close to each other
the arms are straight by the sides
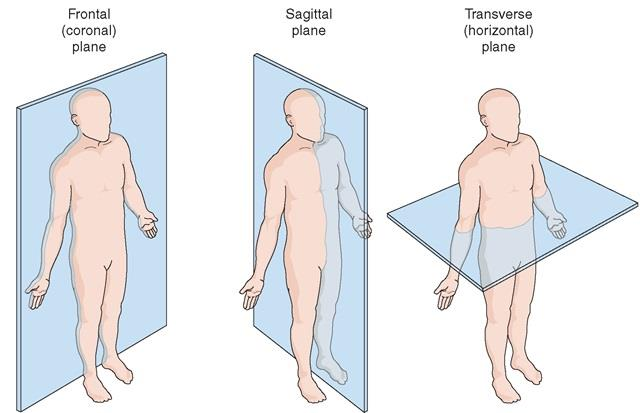
Anatomical planes
Sagittal plane: A vertical plane divides the body into right and left parts.
Median sagittal plane: The plane passing through the center of the body dividing it into right & left halves
Parasagittal plane: Plane lying to one or the other side of the median plane & parallel to it. • It divides the body into unequal parts.
Coronal plane: A vertical plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Transverse plane: A horizontal plane divides the body into upper (cranial) and lowers (caudal) parts
Anatomical terms:
- Terms related to the position
Superior: Toward the head.
Inferior: Toward the feet.
Anterior: Toward the front of the body.
Posterior: Toward the back of the body.
Median: At the middle line of the body.
Medial: Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral: Toward the side of the body.
Superficial: Toward the surface of the body.
Deep: Away from the surface of the body.
Proximal: Toward the root of the limb
e.g.: the arm is proximal to the forearm.
Distal: Away from the root of the limb
e.g.: the hand is distal to the forearm.Internal: Inside an organ or cavity.
External: Outside an organ or cavity.

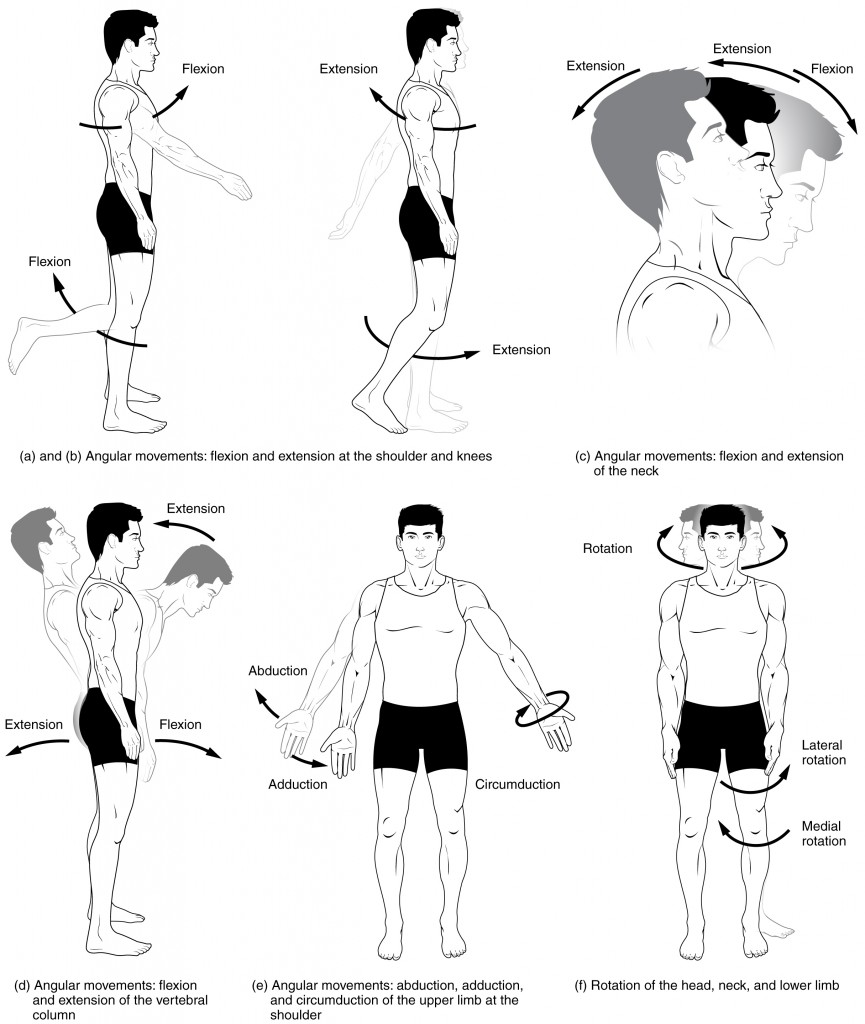
- Terms related to movements
Flexion: a bending movement around a joint that decreases the angle between the two articulating bones.
Extension: an unbending movement around a joint that increases the angle between the two articulating bones.
Abduction: movement away from the midline of the body.
Adduction: movement toward the midline of the body plane.
Elevation: movement upwards.
Depression: movement downwards.
Rotation: Is the movement of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis.
Medial rotation: rotation of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis towards the midline
Lateral rotation: rotation of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis away from the midline.
Circumduction: movement of a limb or extremity so that the distal end describes a circle, it is a successive movement of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction.
Protraction and retraction: These are mostly used to describe the forward and backward movement of the mandible at the temporal-mandibular joint.
Protraction: Is to move forward.
Retraction: Is to move backward.
Body organization
the body of the living organism consists of many systems.
Each system is formed of many organs.
Each organ is formed of many tissues.
Each tissue is formed of layers or groups of similar cells that perform a common function.
The cell is the basic structural and functional component of the body. Each cell is composed of cytoplasm and a nucleus and is surrounded by cell membranes.
Body regions
The human body is divided into several regions that can be identified on the surface of the body. The major body regions are the head, neck, trunk, upper extremity, and lower extremity. The trunk is frequently divided into the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis.
Body systems
The main systems of the human body are as follows:
Cardiovascular / Circulatory system
It is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells and carrying their waste products away.
Digestive system
It is responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients and the elimination of waste from the body.
Endocrine system
It provides chemical communications within the body using hormones.
Integumentary system
It includes skin, and its appendages (hair, nails).
Lymphatic system
It defends the body against disease-causing agents.
Musculoskeletal (locomotor) system
It enables the body to move using muscles.
It supports the body and its organs.
Nervous system
It collects information from the senses and tells the muscles to contract.
Urinary system
It is the system where the kidneys filter blood.
Reproductive system
It is responsible for the production of offspring.
Respiratory system
It brings air into the body to oxygenate the blood.
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomy: The study of the body's structures and the relationship of its parts to each other.
Anatomical Position
the anatomical position is the standard reference position of the body
the body is in an erect posture
the face and the palms are facing forward
the feet close to each other
the arms are straight by the sides

Anatomical planes
Sagittal plane: A vertical plane divides the body into right and left parts.
Median sagittal plane: The plane passing through the center of the body dividing it into right & left halves
Parasagittal plane: Plane lying to one or the other side of the median plane & parallel to it. • It divides the body into unequal parts.
Coronal plane: A vertical plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Transverse plane: A horizontal plane divides the body into upper (cranial) and lowers (caudal) parts

Anatomical terms:
- Terms related to the position
Superior: Toward the head.
Inferior: Toward the feet.
Anterior: Toward the front of the body.
Posterior: Toward the back of the body.
Median: At the middle line of the body.
Medial: Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral: Toward the side of the body.
Superficial: Toward the surface of the body.
Deep: Away from the surface of the body.
Proximal: Toward the root of the limb
e.g.: the arm is proximal to the forearm.
Distal: Away from the root of the limb
e.g.: the hand is distal to the forearm.Internal: Inside an organ or cavity.
External: Outside an organ or cavity.

- Terms related to movements
Flexion: a bending movement around a joint that decreases the angle between the two articulating bones.
Extension: an unbending movement around a joint that increases the angle between the two articulating bones.
Abduction: movement away from the midline of the body.
Adduction: movement toward the midline of the body plane.
Elevation: movement upwards.
Depression: movement downwards.
Rotation: Is the movement of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis.
Medial rotation: rotation of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis towards the midline
Lateral rotation: rotation of a part of the body around its longitudinal axis away from the midline.
Circumduction: movement of a limb or extremity so that the distal end describes a circle, it is a successive movement of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction.
Protraction and retraction: These are mostly used to describe the forward and backward movement of the mandible at the temporal-mandibular joint.
Protraction: Is to move forward.
Retraction: Is to move backward.

Body organization
the body of the living organism consists of many systems.
Each system is formed of many organs.
Each organ is formed of many tissues.
Each tissue is formed of layers or groups of similar cells that perform a common function.
The cell is the basic structural and functional component of the body. Each cell is composed of cytoplasm and a nucleus and is surrounded by cell membranes.
Body regions
The human body is divided into several regions that can be identified on the surface of the body. The major body regions are the head, neck, trunk, upper extremity, and lower extremity. The trunk is frequently divided into the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis.
Body systems
The main systems of the human body are as follows:
Cardiovascular / Circulatory system
It is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells and carrying their waste products away.
Digestive system
It is responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients and the elimination of waste from the body.
Endocrine system
It provides chemical communications within the body using hormones.
Integumentary system
It includes skin, and its appendages (hair, nails).
Lymphatic system
It defends the body against disease-causing agents.
Musculoskeletal (locomotor) system
It enables the body to move using muscles.
It supports the body and its organs.
Nervous system
It collects information from the senses and tells the muscles to contract.
Urinary system
It is the system where the kidneys filter blood.
Reproductive system
It is responsible for the production of offspring.
Respiratory system
It brings air into the body to oxygenate the blood.
 Knowt
Knowt