
Ch 5 - Supply
Supply: the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply at different prices in a given time period
Law of supply: as the price of a product rises, the quantity supplied of the product will eventually increase
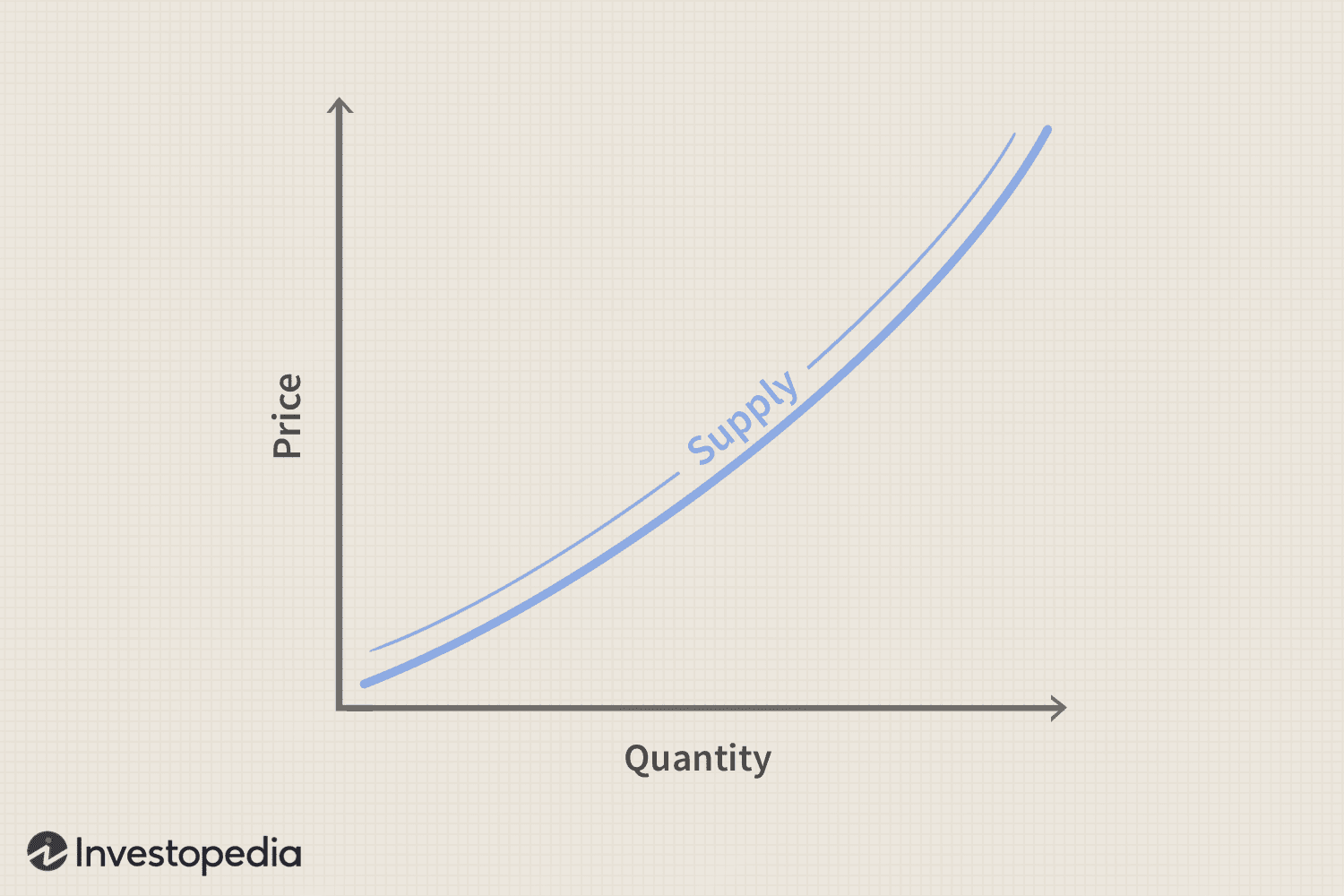
The supply curve normally slopes upwards
Price rises but costs don't change → profitability increases → supply more
Supply curve: represents the relationship between the price and the quantity supplied of a product
Non-price determinants of supply:
Changes in factors of production: (supply shifts to left) → land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
Improvements in tech (supply shifts to the right)
Expectations: supply increases if product is expected to gain profit
Indirect taxes → increase costs → supply shifts left
Competition: if another product is produced with higher profit, supply for existing product decreases
Subsidies → reduce costs → supply shifts right
More firms → supply shifts to the right → more being supplied at each price level
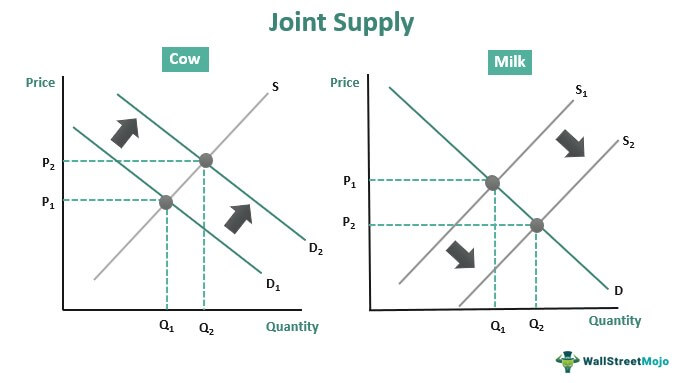
Joint supply:
The law of diminishing marginal returns: as more variable factors are added to a given quantity fixed factors, holding tech constant, marginal product eventually drops
Fixed factor: employment remains constant
Variable factor : employment increases as output increases
Short run: period with fixed + variable factors
firms can expand output by employing variable factors only
Long run: period when all factors are variable
firms can expand output by increasing the use of all factors
Marginal Product (MP): change in total product as a result of change in input
Formula: MP of the nth unit = TP of n units - TP of (n-1) units
MP = △TP /△V
Why does this happen?
Workers fully utilise fixed factors initially so MP rises
when more workers are added, too many workers relative to the amount of fixed factors, MP eventually drops
Total product: total output that a firm producers using variable and fixed factors in a given time period
Average product: output that is produced, an average, by each unit of the variable factors
Formula: AP = TPV
Rules:
As supply increases, price decreases, and demand increases
As supply decreases, price increases, and demand decreases
Ch 5 - Supply
Supply: the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply at different prices in a given time period
Law of supply: as the price of a product rises, the quantity supplied of the product will eventually increase
The supply curve normally slopes upwards
Price rises but costs don't change → profitability increases → supply more
Supply curve: represents the relationship between the price and the quantity supplied of a product

Non-price determinants of supply:
Changes in factors of production: (supply shifts to left) → land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
Improvements in tech (supply shifts to the right)
Expectations: supply increases if product is expected to gain profit
Indirect taxes → increase costs → supply shifts left
Competition: if another product is produced with higher profit, supply for existing product decreases
Subsidies → reduce costs → supply shifts right
More firms → supply shifts to the right → more being supplied at each price level
Joint supply:

The law of diminishing marginal returns: as more variable factors are added to a given quantity fixed factors, holding tech constant, marginal product eventually drops
Fixed factor: employment remains constant
Variable factor : employment increases as output increases
Short run: period with fixed + variable factors
firms can expand output by employing variable factors only
Long run: period when all factors are variable
firms can expand output by increasing the use of all factors
Marginal Product (MP): change in total product as a result of change in input
Formula: MP of the nth unit = TP of n units - TP of (n-1) units
MP = △TP /△V
Why does this happen?
Workers fully utilise fixed factors initially so MP rises
when more workers are added, too many workers relative to the amount of fixed factors, MP eventually drops
Total product: total output that a firm producers using variable and fixed factors in a given time period
Average product: output that is produced, an average, by each unit of the variable factors
Formula: AP = TPV
Rules:
As supply increases, price decreases, and demand increases
As supply decreases, price increases, and demand decreases
 Knowt
Knowt
