
Conduction, Convection and Radiation notes
Thermal energy will always be transferred from hotter areas to colder areas.
This always happens by the processes of:
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Objects will always lose heat until they are in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings: eg. a mug of hot tea will cool down until it reaches room temperature.
Conduction
Conduction is the main method of thermal energy transfer in solids.
Metals are extremely good at conducting heat→ They have an additional method of conduction: free delocalised electrons can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material and hence transfer heat through the metal very quickly.
Solids are also good conductors because the particles are close together and bonds are strong, making transfer of KE more rapid.
In fact, diamond, a non-metal, is also an excellent conductor because it has very strong intermolecular bonds.
Non-metals, liquids and gases are poor at conducting: Poor conductors are called insulators.
In fact, materials containing small pockets of trapped air are especially good at insulating, as air is a gas and so a poor conductor
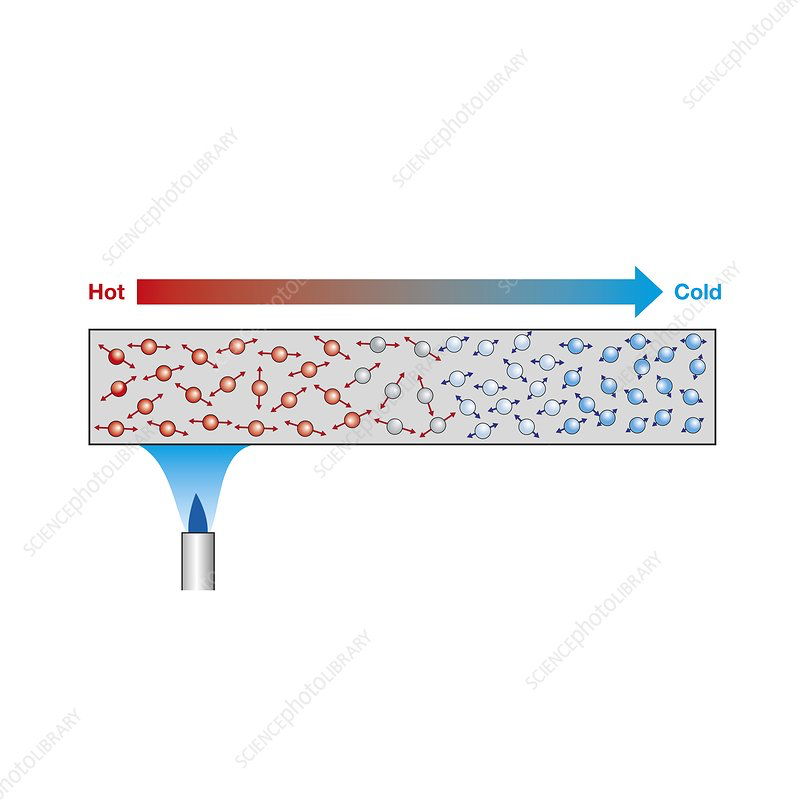
When a substance is heated, the atoms start to vibrate more.
They bump into each other, transferring energy from atom to atom
Intermolecular forces allo the atoms to pass vibrations from one to another
The stronger the forces, the faster the vibrations are passed
Convection
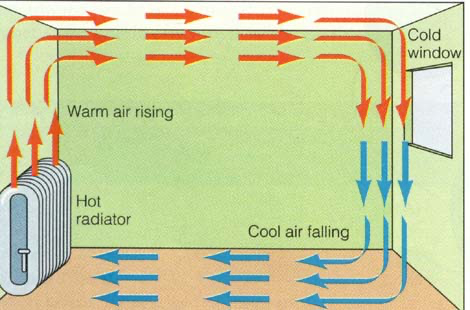
Convection in the transfer of heat through fluids (liquids and gases); it cannot occur in solids.
When a fluid is heated:
Molecules push each other apart, making the fluid expand
The hot fluid becomes less dense than the surroundings
The hot fluid rises, and the cooler surrounding fluid moves in to take its place
Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again
This is called a convection current
Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is the transfer of heat energy by infrared (IR) waves.
All bodies, no matter what temperature, emit a spectrum of thermal radiation in the form of IR waves.
Radiation is the only type of heat transfer that can travel through a vacuum.
Gases allow radiation through better than liquids, liquids better than solids.
The hotter object, the more infrared radiation it emits in a given time.
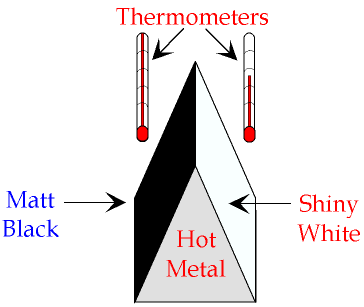
Colours and surfaces affect how well a body emits and absorbs thermal radiation:
Black objects are the best at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation
Shiny objects are the worst at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation
Conduction, Convection and Radiation notes
Thermal energy will always be transferred from hotter areas to colder areas.
This always happens by the processes of:
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Objects will always lose heat until they are in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings: eg. a mug of hot tea will cool down until it reaches room temperature.
Conduction
Conduction is the main method of thermal energy transfer in solids.
Metals are extremely good at conducting heat→ They have an additional method of conduction: free delocalised electrons can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material and hence transfer heat through the metal very quickly.
Solids are also good conductors because the particles are close together and bonds are strong, making transfer of KE more rapid.
In fact, diamond, a non-metal, is also an excellent conductor because it has very strong intermolecular bonds.
Non-metals, liquids and gases are poor at conducting: Poor conductors are called insulators.
In fact, materials containing small pockets of trapped air are especially good at insulating, as air is a gas and so a poor conductor
When a substance is heated, the atoms start to vibrate more.
They bump into each other, transferring energy from atom to atom
Intermolecular forces allo the atoms to pass vibrations from one to another
The stronger the forces, the faster the vibrations are passed

Convection
Convection in the transfer of heat through fluids (liquids and gases); it cannot occur in solids.
When a fluid is heated:
Molecules push each other apart, making the fluid expand
The hot fluid becomes less dense than the surroundings
The hot fluid rises, and the cooler surrounding fluid moves in to take its place
Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again
This is called a convection current

Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is the transfer of heat energy by infrared (IR) waves.
All bodies, no matter what temperature, emit a spectrum of thermal radiation in the form of IR waves.
Radiation is the only type of heat transfer that can travel through a vacuum.
Gases allow radiation through better than liquids, liquids better than solids.
The hotter object, the more infrared radiation it emits in a given time.
Colours and surfaces affect how well a body emits and absorbs thermal radiation:
Black objects are the best at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation
Shiny objects are the worst at emitting and absorbing thermal radiation

 Knowt
Knowt
