
PLANT and ANIMAL CELLS Study Guide
Plant and Animal Cells
A- Cells are the basic unit of all living things. Cells are living things because they grow, reproduce, and take in nutrients. Cells also have genetic material called DNA needed to make new cells. **Unicellular (**single-celled) organisms are made up of only one cell. An amoeba is an example of a unicellular organism. Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. People, dogs, and plants are all examples of multicellular organisms. They are so small they can not be seen with the naked eye. Light microscopes allow us to see cells. With the help of slides to make thin layers of cells and hold them in place, we can zoom in up to 1,000 times the size of the specimen on a slide. Scientists study cells to help identify causes for diseases, which ultimately can lead to cures.
B- Not all cells are the same. Cells are specialized based on their function, meaning that cells can have different purposes. For example, a nerve cell looks very different from a muscle cell due to their different functions. Cells have many different parts, called organelles. Some examples include, the nucleus, the cytoplasm, the cell membrane and/or the cell wall, the vacuole, and the mitochondria. Each organelle has a specific function to help keep the cell alive. Animal and plant cells have many of the same organelles with a few exceptions. Plant cells have a cell wall, along with the cell membrane, to help give the plant a rigid (stiff) structure. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts; the organelles where photosynthesis takes place. All the organelles work together to keep the cell alive. If there was no nucleus the cell wouldn’t be able to grow or reproduce. If there was no mitochondria, it would have no energy and if there were no cell membrane, there wouldn’t be any cell at all.
C-. Vocabulary
cell - the smallest part of a living thing that can carry out all the processes of life
microscope - tool that makes tiny objects appear much larger
cell membrane - a covering that surrounds and protects a cell and protects what enters and leaves it
cytoplasm - “cell liquid” ; a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell
nucleus - controls most cell activities and contains genetic material
organelle - a group of small structures that do certain jobs in a cell
cell wall - stiff covering outside the cell membrane of a plant cell
chloroplasts - an organelle in plant cells that uses light energy to make food
unicellular - made up of only one cell
multicellular - made up of more than one cell
Cell Part | Function | Plants | Animals |
|---|---|---|---|
Nucleus | Controls most cell activitiesContains genetic material | present | present |
Cell membrane | Protects cellControls what enters and leaves the cell | present | present |
cytoplasm | Contains organelles | present | present |
mitochondria | powerhouse; makes energy | present | present |
Cell wall | Supports cell | present | Not present |
chloroplasts | Uses sun’s energy to make food for cell | present | Not present |
Animal Cell 
Plant Cell 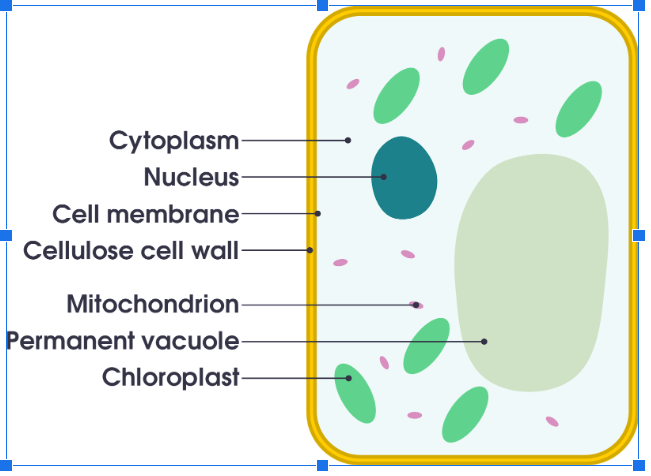
PLANT and ANIMAL CELLS Study Guide
Plant and Animal Cells
A- Cells are the basic unit of all living things. Cells are living things because they grow, reproduce, and take in nutrients. Cells also have genetic material called DNA needed to make new cells. **Unicellular (**single-celled) organisms are made up of only one cell. An amoeba is an example of a unicellular organism. Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. People, dogs, and plants are all examples of multicellular organisms. They are so small they can not be seen with the naked eye. Light microscopes allow us to see cells. With the help of slides to make thin layers of cells and hold them in place, we can zoom in up to 1,000 times the size of the specimen on a slide. Scientists study cells to help identify causes for diseases, which ultimately can lead to cures.
B- Not all cells are the same. Cells are specialized based on their function, meaning that cells can have different purposes. For example, a nerve cell looks very different from a muscle cell due to their different functions. Cells have many different parts, called organelles. Some examples include, the nucleus, the cytoplasm, the cell membrane and/or the cell wall, the vacuole, and the mitochondria. Each organelle has a specific function to help keep the cell alive. Animal and plant cells have many of the same organelles with a few exceptions. Plant cells have a cell wall, along with the cell membrane, to help give the plant a rigid (stiff) structure. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts; the organelles where photosynthesis takes place. All the organelles work together to keep the cell alive. If there was no nucleus the cell wouldn’t be able to grow or reproduce. If there was no mitochondria, it would have no energy and if there were no cell membrane, there wouldn’t be any cell at all.
C-. Vocabulary
cell - the smallest part of a living thing that can carry out all the processes of life
microscope - tool that makes tiny objects appear much larger
cell membrane - a covering that surrounds and protects a cell and protects what enters and leaves it
cytoplasm - “cell liquid” ; a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell
nucleus - controls most cell activities and contains genetic material
organelle - a group of small structures that do certain jobs in a cell
cell wall - stiff covering outside the cell membrane of a plant cell
chloroplasts - an organelle in plant cells that uses light energy to make food
unicellular - made up of only one cell
multicellular - made up of more than one cell
Cell Part | Function | Plants | Animals |
|---|---|---|---|
Nucleus | Controls most cell activitiesContains genetic material | present | present |
Cell membrane | Protects cellControls what enters and leaves the cell | present | present |
cytoplasm | Contains organelles | present | present |
mitochondria | powerhouse; makes energy | present | present |
Cell wall | Supports cell | present | Not present |
chloroplasts | Uses sun’s energy to make food for cell | present | Not present |
Animal Cell 
Plant Cell 
 Knowt
Knowt