
Origins of the Cold War
Starts around 1945 and ends around 1992 (some stay we are still involved in the war today)
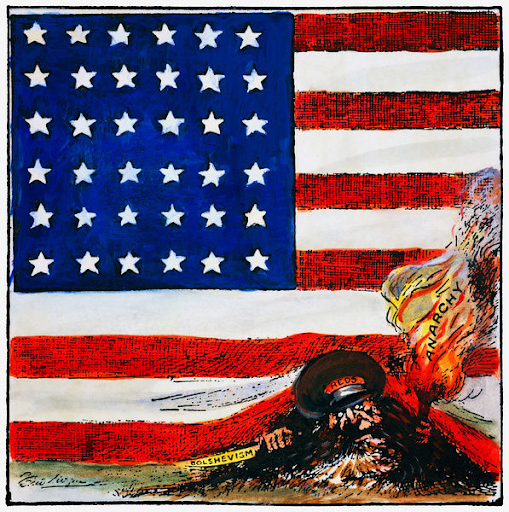

The reds are coming in with a knife and fire to destroy the United States. Instills fear and intimidation among US citizens.
United States | Soviet Union | |
|---|---|---|
Deaths | Loss about 400,000 lives in World War II | Loss more than 20,000,000 lives in World War II |
IdealogyUS - DemocracySoviet Union - Dictatorship | Encourage democracy in other countries to help prevent the rise of Communist governments | Encourage communism in other countries as part of a worldwide workers’ revolution |
Goals- The US wants to rebuild economy- The Soviet Union wants to rebuild their country | Gain access to raw materials and markets to fuel booming industries | Rebuild its war–ravaged economy using Eastern Europe’s industrial equipment and raw materials |
Germany- The US wants to stabilize Germany so that trade continues and war is prevented | Reunite Germany to stabilize it and increase the security of Europe | Keep Germany divided to prevent its waging war again |
Russia and the United States were only united during World War II because they were both fighting against Germany. After Germany is out of the picture, there is nothing left for them to relate to.
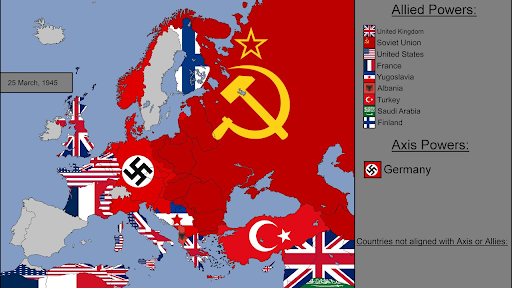
The map shows us where German territory had been. It is between the Soviet Union and the US and it’s allies.
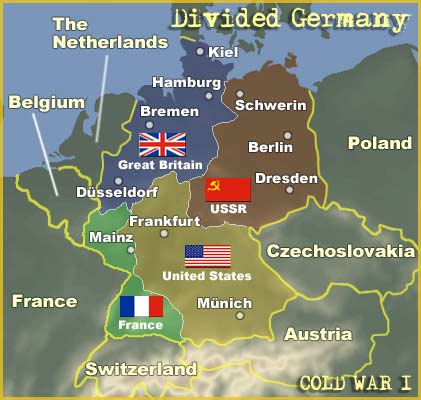
The Iron Curtain Divides East and West
Germany was split into two sections
Soviets controlled (made communist) the Eastern Part of Germany, including Berlin
German Democratic Republic
Berlin was also divided in half because it is the capital
West Berlin was surrounded by communism
Western zones were democratic
Federal Republic of Germany
Iron Curtain Speech
All of these beautiful Eastern European cities can be in danger of the Soviets taking them over
Iron Curtain is a metaphor
shows the uncertainty of what is on the other side of the curtain
Churchill is making sure the US does not return to its isolationist policies
Postwar Foreign Policy
Truman launched the nation into a global battle against communism.
Foreign Policy: Containment
Directed at blocking Soviet influences and stopping the expansion of communism
For alliances and helping weak countries resist Soviet advances
Truman Doctrine
U.S. should assist other nations that were facing external pressure or internal revolution.
Truman support for countries that rejected communism
Controversial
Congress authorized more than $400 million in aid to Turkey and Greece
Marshall Plan
Committing the United States to help in the rebuilding of post – World War II Europe.
Aid given to needy European countries
Provide food, machinery, and other materials to rebuild Western Europe
Spectacular success
Berlin Airlift – 1ˢᵗ Major Crisis
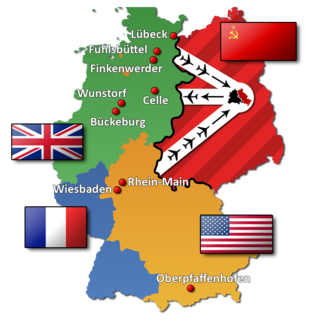
The Soviets do not want the United States in Berlin anymore, so they start building the Berlin Blockade around West Berlin.
B52 bombers are used to drop off food and supplies to West Berlin. This was done for over a year.
Soviet Union eventually takes down the Berlin Blockade.
Cold War Divides the World
Cold War is a struggle over political differences carried on by means short of military action or war
A cold war is about tension, spying, propaganda, diplomacy and secret operations
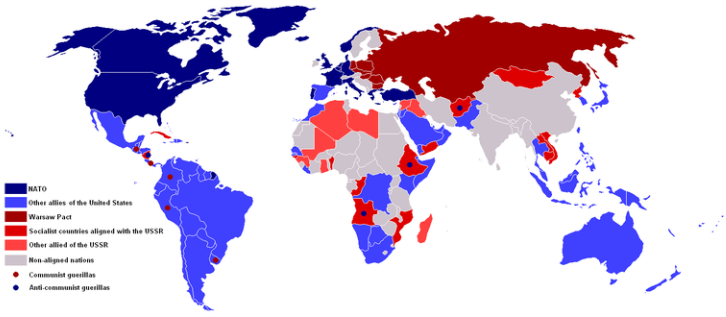
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) – U.S.A & Canada joined with ten western European nations
Strong alliance
Warsaw Pact
Rival to NATO which included: Soviet Union, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania
Threat of Nuclear War
Only four years later, the Soviet Union begins testing nuclear weapons
MAD - Mutually Assured Destruction
If any nation used a nucluear bomb then everything on Earth would be destroyed
Brinkmanship is a policy to go to towards the edge of war
We had to show that we were willing to take things as far as we could
Nato vs Warsaw Pact
Origins of the Cold War
Starts around 1945 and ends around 1992 (some stay we are still involved in the war today)

The reds are coming in with a knife and fire to destroy the United States. Instills fear and intimidation among US citizens.
United States | Soviet Union | |
|---|---|---|
Deaths | Loss about 400,000 lives in World War II | Loss more than 20,000,000 lives in World War II |
IdealogyUS - DemocracySoviet Union - Dictatorship | Encourage democracy in other countries to help prevent the rise of Communist governments | Encourage communism in other countries as part of a worldwide workers’ revolution |
Goals- The US wants to rebuild economy- The Soviet Union wants to rebuild their country | Gain access to raw materials and markets to fuel booming industries | Rebuild its war–ravaged economy using Eastern Europe’s industrial equipment and raw materials |
Germany- The US wants to stabilize Germany so that trade continues and war is prevented | Reunite Germany to stabilize it and increase the security of Europe | Keep Germany divided to prevent its waging war again |
Russia and the United States were only united during World War II because they were both fighting against Germany. After Germany is out of the picture, there is nothing left for them to relate to.

The map shows us where German territory had been. It is between the Soviet Union and the US and it’s allies.
The Iron Curtain Divides East and West
Germany was split into two sections
Soviets controlled (made communist) the Eastern Part of Germany, including Berlin
German Democratic Republic
Berlin was also divided in half because it is the capital
West Berlin was surrounded by communism
Western zones were democratic
Federal Republic of Germany

Iron Curtain Speech
All of these beautiful Eastern European cities can be in danger of the Soviets taking them over
Iron Curtain is a metaphor
shows the uncertainty of what is on the other side of the curtain
Churchill is making sure the US does not return to its isolationist policies
Postwar Foreign Policy
Truman launched the nation into a global battle against communism.
Foreign Policy: Containment
Directed at blocking Soviet influences and stopping the expansion of communism
For alliances and helping weak countries resist Soviet advances
Truman Doctrine
U.S. should assist other nations that were facing external pressure or internal revolution.
Truman support for countries that rejected communism
Controversial
Congress authorized more than $400 million in aid to Turkey and Greece
Marshall Plan
Committing the United States to help in the rebuilding of post – World War II Europe.
Aid given to needy European countries
Provide food, machinery, and other materials to rebuild Western Europe
Spectacular success
Berlin Airlift – 1ˢᵗ Major Crisis

The Soviets do not want the United States in Berlin anymore, so they start building the Berlin Blockade around West Berlin.
B52 bombers are used to drop off food and supplies to West Berlin. This was done for over a year.
Soviet Union eventually takes down the Berlin Blockade.
Cold War Divides the World
Cold War is a struggle over political differences carried on by means short of military action or war
A cold war is about tension, spying, propaganda, diplomacy and secret operations
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) – U.S.A & Canada joined with ten western European nations
Strong alliance
Warsaw Pact
Rival to NATO which included: Soviet Union, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania
Threat of Nuclear War
Only four years later, the Soviet Union begins testing nuclear weapons
MAD - Mutually Assured Destruction
If any nation used a nucluear bomb then everything on Earth would be destroyed
Brinkmanship is a policy to go to towards the edge of war
We had to show that we were willing to take things as far as we could
Nato vs Warsaw Pact

 Knowt
Knowt