
Railroads Notes
Growth
Year | Railroads |
|---|---|
1860 | 30,000 |
1890 | 180,000 |
The Good
Growth-Nationwide Markets
Subsidies-Government Pays to Build Railroads
Leads to profit
More money for companies
Jobs-Created thousands of jobs in industries
Early Lines
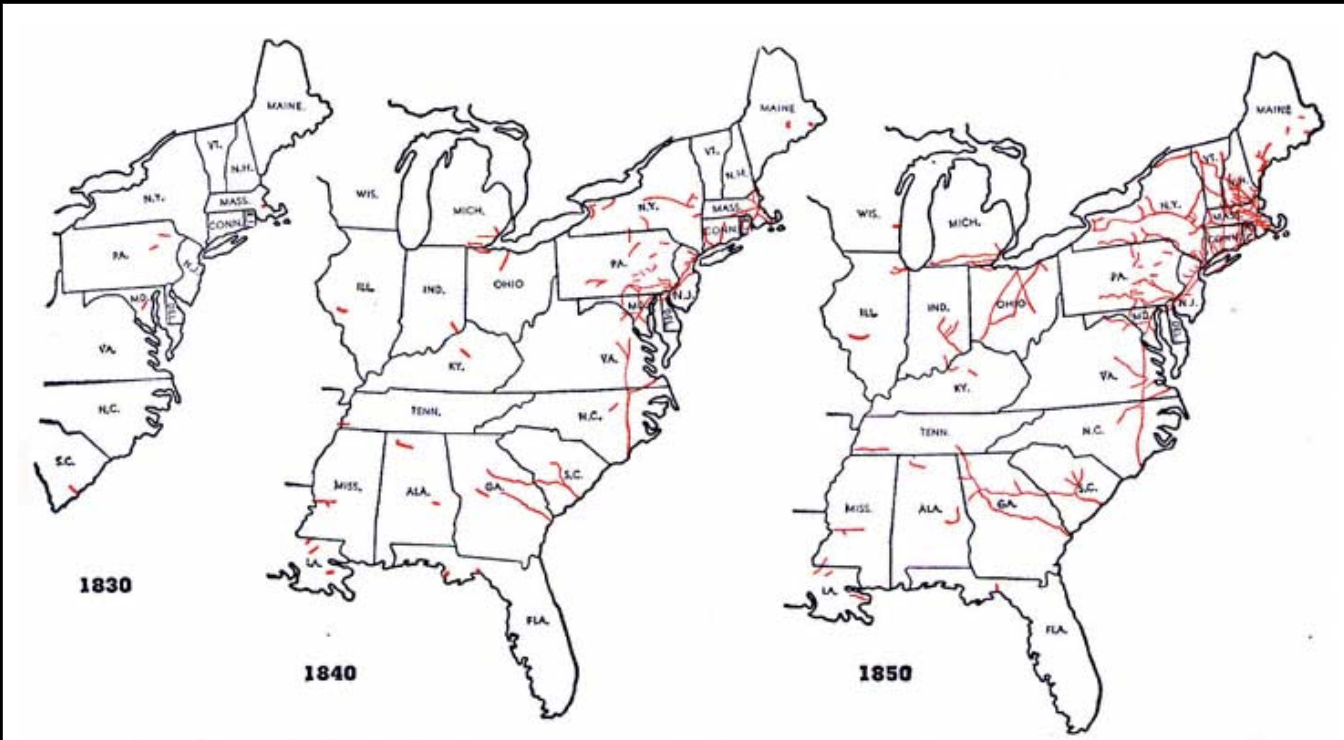
Efficiency
Means more, faster, better
To be more efficient, they
Standardized Gauges
Consolidation-Join Railroads Together
Create a network of rails
Vanderbilt
He created a railroad empire
He consolidated many railroads
Generated a lot of profit
Philanthropy
Many people get rich from railroads
They have extreme wealth
They believe that since they have so much wealth, they should try to improve society
Vanderbilt is an example of this
Civil War

The US Wants to promote growth in the West
They dislike building railroads in the west and center because native Americans reside there
The Transcontinental Railroad (TCRR)
https://junior.scholastic.com/issues/2018-19/051319/the-railroad-that-changed-america.html#1040L
New Rails
Government Paid Money to Build-Favored BB
Paid $16,000 to $48,000 per mile
Union and Central Pacific were the only 2 companies building railroads in this area
The railroads were paid for them by the government
Massive Profit
Government built through Native American Land
There were no rights given to Native Americans
Transcontinental Railroad
Union Pacific - Easier
Starts East
Builds Westward
Central Pacific - Leland Stanford
Starts West
Builds East
Labor
Chinese, Irish, African Americans, Mexicans
No workers rights
Horrible Conditions
Continued Growth
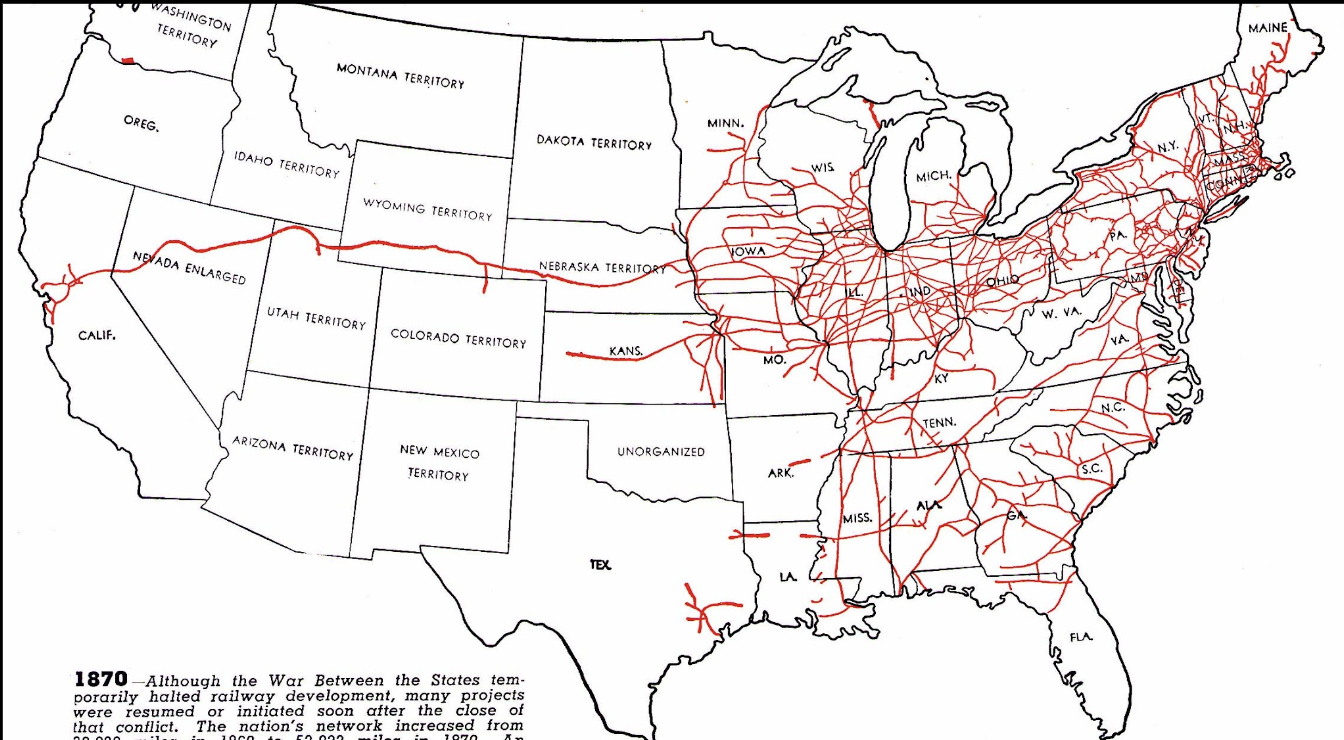
New States Through Settlement

New States Through Settlements

Growth
8 New States were formed
Territories to States based on Population
Demonstrates growth west of the Mississippi
Nationwide Markets
Expanding business across the country
Bigger Businesses
Eww thats Growth
Cut-throat Competition
Favored Larger Companies
They can afford to lose money cutting prices
When competition can’t keep up
Buy them when they go bankrupt
Creates Monopoly
Fix Prices higher to create more profit
No competition-worse for consumer
Pooling
Companies join Together in a region
Everyone Raise Prices
No competitio
Higher Prices
Split Profits
Natural Monopoly
Natural Monopoly - Complete control of an industry due to difficult conditions for competitors to enter an industry
In the south, there wasn’t enough people for competition, creating a natural monopoly
Not enough people for competition
Called Natural Monopoly when there is not enough people to compete
No competition
Higher prices
Worse service
Railroads Notes
Growth
Year | Railroads |
|---|---|
1860 | 30,000 |
1890 | 180,000 |
The Good
Growth-Nationwide Markets
Subsidies-Government Pays to Build Railroads
Leads to profit
More money for companies
Jobs-Created thousands of jobs in industries
Early Lines

Efficiency
Means more, faster, better
To be more efficient, they
Standardized Gauges
Consolidation-Join Railroads Together
Create a network of rails
Vanderbilt
He created a railroad empire
He consolidated many railroads
Generated a lot of profit
Philanthropy
Many people get rich from railroads
They have extreme wealth
They believe that since they have so much wealth, they should try to improve society
Vanderbilt is an example of this
Civil War

The US Wants to promote growth in the West
They dislike building railroads in the west and center because native Americans reside there
The Transcontinental Railroad (TCRR)
https://junior.scholastic.com/issues/2018-19/051319/the-railroad-that-changed-america.html#1040L
New Rails
Government Paid Money to Build-Favored BB
Paid $16,000 to $48,000 per mile
Union and Central Pacific were the only 2 companies building railroads in this area
The railroads were paid for them by the government
Massive Profit
Government built through Native American Land
There were no rights given to Native Americans
Transcontinental Railroad
Union Pacific - Easier
Starts East
Builds Westward
Central Pacific - Leland Stanford
Starts West
Builds East
Labor
Chinese, Irish, African Americans, Mexicans
No workers rights
Horrible Conditions
Continued Growth

New States Through Settlement

New States Through Settlements

Growth
8 New States were formed
Territories to States based on Population
Demonstrates growth west of the Mississippi
Nationwide Markets
Expanding business across the country
Bigger Businesses
Eww thats Growth

Cut-throat Competition
Favored Larger Companies
They can afford to lose money cutting prices
When competition can’t keep up
Buy them when they go bankrupt
Creates Monopoly
Fix Prices higher to create more profit
No competition-worse for consumer
Pooling
Companies join Together in a region
Everyone Raise Prices
No competitio
Higher Prices
Split Profits
Natural Monopoly
Natural Monopoly - Complete control of an industry due to difficult conditions for competitors to enter an industry
In the south, there wasn’t enough people for competition, creating a natural monopoly
Not enough people for competition
Called Natural Monopoly when there is not enough people to compete
No competition
Higher prices
Worse service
 Knowt
Knowt