
Chapter 15 - Support, Movement and Locomotion
Skeletal System
It consists of 3 main types of tissues:
(a) Cartilage
(b) Bones
(c) Muscles
It’s functions are to:
Protection
Support
Muscle attachment
Movement
Storage of calcium
Blood cells formation
Skeleton of Humans
Axial Skeleton (Skull, back bone, ribs)
Appendicular Skeleton (Limbs)
Girdles (pelvic girdle, shoulder girdle)
Skull : The most anterior part of the body. It encloses and protects the brain. It also holds and protects the main sense organ.
Backbone: It makes the central axis of the body. It keeps us upright and holds the weight of body. It is made of 33 irregular bones stacked one above the other.
Ribs: Encloses and protects the heart, lungs and major blood vessels. They also move to bring inhalation and exhale.
Shoulder Bone: A triangular, flat bone with a shallow cavity on narrower end. It joints the arm to the axial skeleton.
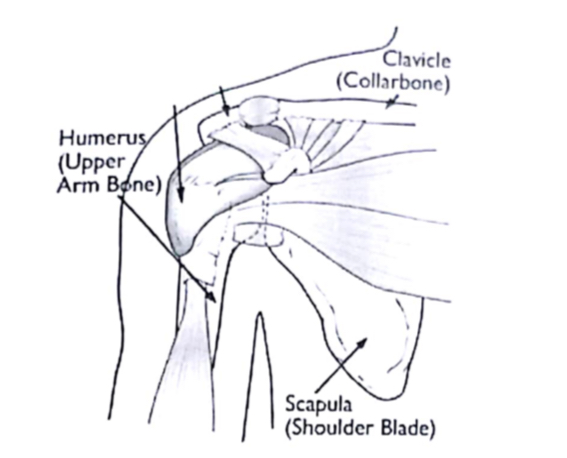
Collar Bone: It prevents the shoulder from bending inward
Ulna and Radius:
Ulna is longer than radius
Ulna is thicker than radius
Ulna has cavity where part of humerus fitted to make hinge joint.
Ulna has an extended bone
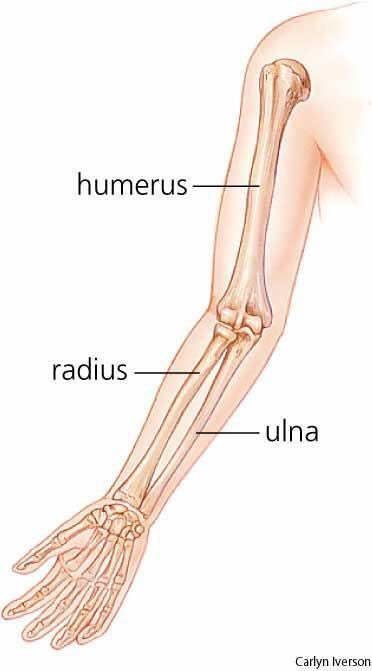
Humerus: A long bone with a rounded head epiphysis and a long central shaft called endophysis.
Joints:
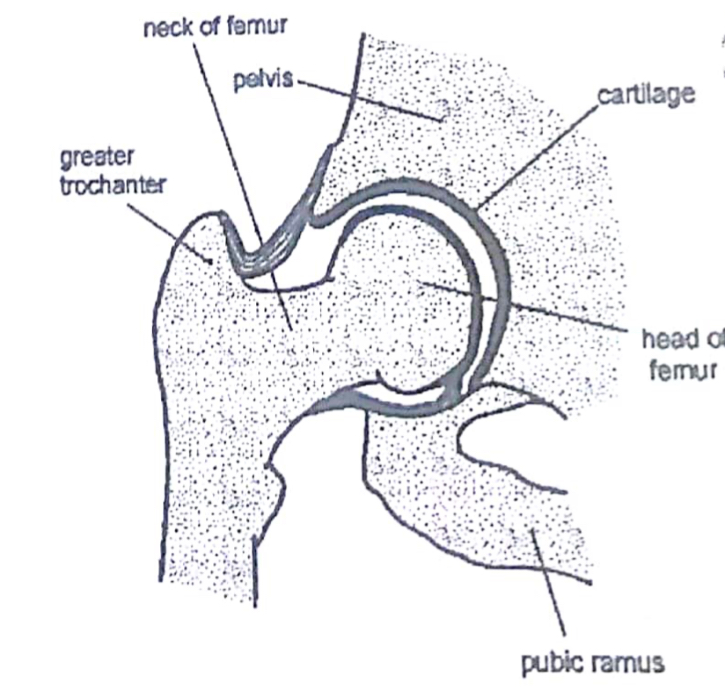
Ball and Socket: moves 360 degrees in all planes.
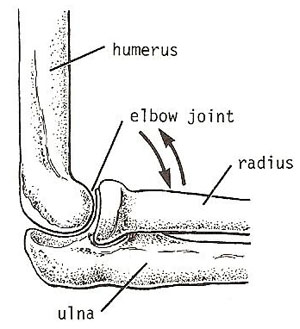
Hinge Joint: function like the hinge on a door, allowing bones to move in one direction back and forth with limited motion along other planes.
Antagonistic Muscles:
Muscles contract and pull the bones. They can never push bones back.
When the muscles contract they shorten in length.
To move a bone at a joint, muscles contract. They are arranged in pairs called antagonistic pairs i.e. when one contracts, the other relaxes.
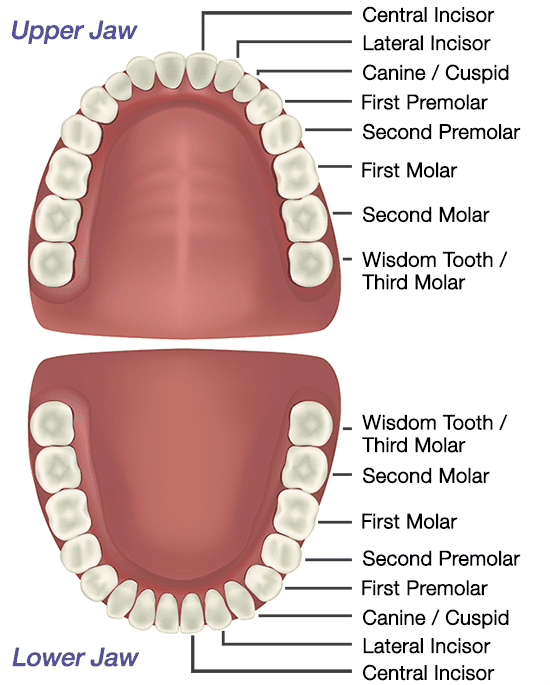
Teeth
Types of Teeth:
Incisors (8 in number)
- The front four teeth on each jaw.
- It is used for biting and cutting the food.
Canines (4 in number)
- One sharp/ pointed tooth on either side of both of the jaws next to the incisors.
- It is used for cracking nuts
Premolars (8 in number)
- Two premolars next to incisors on either side of both the jaws. On the lower jaw they have two roots whereas on the upper jaw, a single root. The crown has cusps which increase surfaces that come in contact for grinding.
Molars
- 3 molars next to premolars on both sides of each jaw.
Causes of Dental Decay:
Intake of sugary foods
Oral unhygienic
Food, bacteria and mucus deposited on teeth as plaque
Bacteria break down sugars to make acids
Acids decrease pH of the mouth
It corrodes the surface of teeth
The minerals deposit in the plaque
Plaque is hardened to tartar which is not removed by simple brushing.
Tartar roughens the surface of teeth
More food deposits. More breakdown of food anaerobically lower pH further
It keeps on eroding the enamel
Enamel is a harder tissue. It takes longer to be eroded, however once it is eroded, denting is exposed, which makes a tooth sensitive to hot and cold.
Erosion of denting exposes pulp, which makes the tooth painful.
Prevention of Dental Diseases:
brushing regularly
Dental floss
Regular visits to dentist
Cut down sugar intake
Use of fluoride tooth paste
Scaling
Use of fluoridated water
Dietary fibers
Chapter 15 - Support, Movement and Locomotion
Skeletal System
It consists of 3 main types of tissues:
(a) Cartilage
(b) Bones
(c) Muscles
It’s functions are to:
Protection
Support
Muscle attachment
Movement
Storage of calcium
Blood cells formation
Skeleton of Humans
Axial Skeleton (Skull, back bone, ribs)
Appendicular Skeleton (Limbs)
Girdles (pelvic girdle, shoulder girdle)
Skull : The most anterior part of the body. It encloses and protects the brain. It also holds and protects the main sense organ.
Backbone: It makes the central axis of the body. It keeps us upright and holds the weight of body. It is made of 33 irregular bones stacked one above the other.
Ribs: Encloses and protects the heart, lungs and major blood vessels. They also move to bring inhalation and exhale.
Shoulder Bone: A triangular, flat bone with a shallow cavity on narrower end. It joints the arm to the axial skeleton.

Collar Bone: It prevents the shoulder from bending inward
Ulna and Radius:
Ulna is longer than radius
Ulna is thicker than radius
Ulna has cavity where part of humerus fitted to make hinge joint.
Ulna has an extended bone

Humerus: A long bone with a rounded head epiphysis and a long central shaft called endophysis.
Joints:
Ball and Socket: moves 360 degrees in all planes.

Hinge Joint: function like the hinge on a door, allowing bones to move in one direction back and forth with limited motion along other planes.

Antagonistic Muscles:
Muscles contract and pull the bones. They can never push bones back.
When the muscles contract they shorten in length.
To move a bone at a joint, muscles contract. They are arranged in pairs called antagonistic pairs i.e. when one contracts, the other relaxes.
Teeth
Types of Teeth:
Incisors (8 in number)
- The front four teeth on each jaw.
- It is used for biting and cutting the food.
Canines (4 in number)
- One sharp/ pointed tooth on either side of both of the jaws next to the incisors.
- It is used for cracking nuts
Premolars (8 in number)
- Two premolars next to incisors on either side of both the jaws. On the lower jaw they have two roots whereas on the upper jaw, a single root. The crown has cusps which increase surfaces that come in contact for grinding.
Molars
- 3 molars next to premolars on both sides of each jaw.

Causes of Dental Decay:
Intake of sugary foods
Oral unhygienic
Food, bacteria and mucus deposited on teeth as plaque
Bacteria break down sugars to make acids
Acids decrease pH of the mouth
It corrodes the surface of teeth
The minerals deposit in the plaque
Plaque is hardened to tartar which is not removed by simple brushing.
Tartar roughens the surface of teeth
More food deposits. More breakdown of food anaerobically lower pH further
It keeps on eroding the enamel
Enamel is a harder tissue. It takes longer to be eroded, however once it is eroded, denting is exposed, which makes a tooth sensitive to hot and cold.
Erosion of denting exposes pulp, which makes the tooth painful.
Prevention of Dental Diseases:
brushing regularly
Dental floss
Regular visits to dentist
Cut down sugar intake
Use of fluoride tooth paste
Scaling
Use of fluoridated water
Dietary fibers
 Knowt
Knowt