
Earth Science - Universe
Astronomy - The study of extraterrestrial and heavenly bodies.
Cosmology - is a branch of astronomy that involves the origin and evolution of the universe, from the Big Bang to today and on into the future.
Cosmogony- This term refers to origin of the universe specifically the solar system.
THEORIES ON THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
Oscillating Universe Theory
Proposed that the universe currently exists between the big bang and the big crunch (one of the predicted ends of the universe)
Big Crunch is one of the possible scenarios of the end of the universe where the universe is predicted to shrink and eventually collapse on itself.
Eternal Inflation Theory
Supposes that instead of ending in a big crunch as the oscillating universe, the inflation never stops.
Steady State Theory
Assumed that the universe has always been and will always be the same.
The idea was based on the cosmological principle that the universe is uniform in space and has unchanging time.
Multiverse Theory
Andrei Linde proposed that the universe is as just one many “bubbles” that grew as part of the multiverse.
Creation Story
All life forms existing today on Earth have been created by a supreme being-God.
Rigveda Theory
It describes the universe as an oscillating universe in which a "cosmic egg" or Brahmanda, containing the whole universe expands out of a single concentrated point called Bindu (point or dot), and will eventually collapse again.
An ancient Indian Collection of more the one thousand Vedic Sanskrit hymns
Atomic Universe
Leucippus and Democritus proposed this theory.
They held that the universe was composed of very small, indivisible, and indestructible atoms.
They held that the universe was composed of very small, indivisible, and indestructible atoms.
The universe is like a giant living body, with the sun and the stars as the most important parts to which everything else were interconnected.
Main subatomic particles: Protons(positive), electrons(negative), Neutrons (Neutral)
Primordial Universe of Anaxagoras
The original state of the cosmos was a primordial mixture of all its ingredients which existed in infinitesimally small fragments of themselves.
The mixture was not entirely uniform; some ingredients were present in higher concentrations than others, and the distribution of these ingredients very from place to place.
Aristotelian & Ptolemaic Universe
The earth does not revolve or rotate on its own axis.
“Earth is the center of the Solar System”
Copernican Universe
“Sun is the center of the Solar System”
Big Bang Theory
The big bang is the event about 13.7 billion years ago when time, space, matter, and energy came into existence.
This event started form a hot, dense state called singularity that has undergone inflation (a short but rapid expansion) to become the universe that is known today.
It is not an explosion but rather an expansion of space.
@@Two earliest elements that was discovered:@@Helium and Hydrogen.
Timeline of the Big Bang
Matter era
Radiation era
Planck Epoch
All things are compressed in the singularity.
Temperature is very hot (10³²k)
What are these forces?
1. Gravity
2. Electromagnetic
3. Strong nuclear force
4. Weak nuclear force

Grand Unification
Estimated time will be around 10-36s.
Gravity was separated from the unification.
Elementary particles were forms like quarks and electrons.
Inflationary Epoch
Electroweak Epoch
Estimated time will be around 10-³² to 10–⁶ s.
Strong nuclear force was separated causing the expansion of the singularity.
It is followed by EM and Weak force.
Quark Epoch
Estimated time will be around 10-⁶ s.
Quark and antiquark will annihilate each other returning energy back to space.
Hadron Epoch
Lepton Epoch
Estimated time will be around 1s to 3 mins.
Quarks combined to form protons and neutrons.
Electrons dominated around this time.
Nucleosynthesis Epoch
Estimated time will be around 20 minutes.
Protons and Neutrons fused to form the nucleus of atoms like Helium.
Recombination Epoch
Estimated time will be around 300,000 years.
__Nucleus of the formed elements attracted to be stable and become atom__s.
Galactic Epoch
Estimated time will be around 150 million years.
Time between atoms and star formation.
Although there were photons, the universe is literally dark.
Stellar Epoch
Happened at around 300-500 million years.
First stars were formed. They were massive and short lived.
THEORIES ON THE ORIGIN OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Solar System formation
Happened at around 4.5 billion Years.
Some million years later, earth was formed.
Present Day
13.8 billion years from the Big Bang.
Galaxies are still moving away from each other.
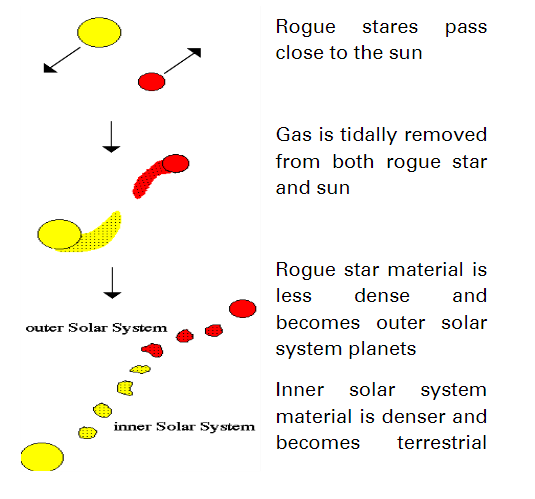
Encounter Hypothesis
a collision happened and huge amounts of gas from the sun explode out of it but more in the same directions around the sun.
It occurs when the sun and a passing star had an encounter.
Materials are pulled from the stellar surfaces, then it cools and condenses forming planetary bodies.
The Nebular Hypothesis
The solar nebula (gas) contracted, cooled, and condensed into dust sized particles that accreted (stuck together as the result of collisions) into protoplanets (Asteroid sized bodies) and then larger planets.
The most accepted model in cosmogony.
states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula
Kant and Laplace proposed the nebular hypothesis over two centuries ago.
Our Solar System formed from a giant, swirling cloud of gas & dust.
The Big Bang Theory is describes a the “all matter and energy once exploded out of a single point”
Electromagnetic force - A force that binds nucleus of an atom.
Protosun - forms in the very center of the accretion disk.
WHY DO SOME SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THAT MARS COULD BE THE FUTURE OF HUMANITY?
Geiod-shaped
Has two major movement:
Rotation –the spinning of the Earth on its axis; causes day and night; starts from East to West
Revolution –occurs as the Earth moves around the Sun
Factors to make a planet habitable:
1.Temperature
Venus -Average temperature: Approximately 471°C (TOO HOT)
Earth -Average temperature: Approximately 14°C(JUST RIGHT)
Mars -Average temperature: Approximately −63 °C (TOO COLD)
The habitable zone corresponds to the range of orbital distance where liquid water can exist on a planet’s surface.
Water
Venus - No water on the surface. Has 0.002% water vapor
Earth - About 71 percent of the Earth's surface is water-covered
Mars - Water still exists in form of polar ice caps.
The presence of water allowed the first photosynthetic organisms to thrive.
Atmosphere
It is a thin layer of gases that hover above our planet's surface, that is held in place by the gravity of that body.
Any planet devoid of an atmosphere would have an average surface temperature below freezing and would experience unpredictable and extreme weather and climates. It would also have an extreme amount of UV radiation because there is no atmosphere that absorbs radiation.
Energy (Heat Energy)
Heat coming from Earth is caused by radiogenic heat from radioactive decay of materials in the core and mantle, and extruded via active tectonic activities, such as volcanism and plate movement.
Heat radiated by the sun is mostly trapped by the atmosphere. This creates the heat needed by organisms on Earth.
Having an atmosphere capable of providing heat like in a greenhouse, the atmosphere is therefore a vital part of photosynthesis.
Earth’s Subsystem
Geosphere
Solid Earth
It is composed of rocks and regolith.
It includes all landforms.
Hydrosphere
It is the totality of Earth’s water
Cryosphere - permanently frozen parts.
Atmosphere
It is the mixture of gases that surrounds a planet
It is composed of 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 0.9% Argon, and 0.10% other gases.
Biosphere
It includes all life forms and even organic matter that has not yet decomposed.


It is the zone where interactions between subsystem is most dynamic.
Earth Science - Universe
Astronomy - The study of extraterrestrial and heavenly bodies.
Cosmology - is a branch of astronomy that involves the origin and evolution of the universe, from the Big Bang to today and on into the future.
Cosmogony- This term refers to origin of the universe specifically the solar system.
THEORIES ON THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
Oscillating Universe Theory
Proposed that the universe currently exists between the big bang and the big crunch (one of the predicted ends of the universe)
Big Crunch is one of the possible scenarios of the end of the universe where the universe is predicted to shrink and eventually collapse on itself.
Eternal Inflation Theory
Supposes that instead of ending in a big crunch as the oscillating universe, the inflation never stops.
Steady State Theory
Assumed that the universe has always been and will always be the same.
The idea was based on the cosmological principle that the universe is uniform in space and has unchanging time.
Multiverse Theory
Andrei Linde proposed that the universe is as just one many “bubbles” that grew as part of the multiverse.
Creation Story
All life forms existing today on Earth have been created by a supreme being-God.
Rigveda Theory
It describes the universe as an oscillating universe in which a "cosmic egg" or Brahmanda, containing the whole universe expands out of a single concentrated point called Bindu (point or dot), and will eventually collapse again.
An ancient Indian Collection of more the one thousand Vedic Sanskrit hymns
Atomic Universe
Leucippus and Democritus proposed this theory.
They held that the universe was composed of very small, indivisible, and indestructible atoms.
They held that the universe was composed of very small, indivisible, and indestructible atoms.
The universe is like a giant living body, with the sun and the stars as the most important parts to which everything else were interconnected.
Main subatomic particles: Protons(positive), electrons(negative), Neutrons (Neutral)
Primordial Universe of Anaxagoras
The original state of the cosmos was a primordial mixture of all its ingredients which existed in infinitesimally small fragments of themselves.
The mixture was not entirely uniform; some ingredients were present in higher concentrations than others, and the distribution of these ingredients very from place to place.
Aristotelian & Ptolemaic Universe
The earth does not revolve or rotate on its own axis.
“Earth is the center of the Solar System”
Copernican Universe
“Sun is the center of the Solar System”
Big Bang Theory
The big bang is the event about 13.7 billion years ago when time, space, matter, and energy came into existence.
This event started form a hot, dense state called singularity that has undergone inflation (a short but rapid expansion) to become the universe that is known today.
It is not an explosion but rather an expansion of space.
@@Two earliest elements that was discovered:@@Helium and Hydrogen.
Timeline of the Big Bang
Matter era
Radiation era
Planck Epoch
All things are compressed in the singularity.
Temperature is very hot (10³²k)
What are these forces?
1. Gravity
2. Electromagnetic
3. Strong nuclear force
4. Weak nuclear force

Grand Unification
Estimated time will be around 10-36s.
Gravity was separated from the unification.
Elementary particles were forms like quarks and electrons.
Inflationary Epoch
Electroweak Epoch
Estimated time will be around 10-³² to 10–⁶ s.
Strong nuclear force was separated causing the expansion of the singularity.
It is followed by EM and Weak force.
Quark Epoch
Estimated time will be around 10-⁶ s.
Quark and antiquark will annihilate each other returning energy back to space.
Hadron Epoch
Lepton Epoch
Estimated time will be around 1s to 3 mins.
Quarks combined to form protons and neutrons.
Electrons dominated around this time.
Nucleosynthesis Epoch
Estimated time will be around 20 minutes.
Protons and Neutrons fused to form the nucleus of atoms like Helium.
Recombination Epoch
Estimated time will be around 300,000 years.
__Nucleus of the formed elements attracted to be stable and become atom__s.
Galactic Epoch
Estimated time will be around 150 million years.
Time between atoms and star formation.
Although there were photons, the universe is literally dark.
Stellar Epoch
Happened at around 300-500 million years.
First stars were formed. They were massive and short lived.
THEORIES ON THE ORIGIN OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Solar System formation
Happened at around 4.5 billion Years.
Some million years later, earth was formed.
Present Day
13.8 billion years from the Big Bang.
Galaxies are still moving away from each other.
Encounter Hypothesis
a collision happened and huge amounts of gas from the sun explode out of it but more in the same directions around the sun.
It occurs when the sun and a passing star had an encounter.
Materials are pulled from the stellar surfaces, then it cools and condenses forming planetary bodies.

The Nebular Hypothesis
The solar nebula (gas) contracted, cooled, and condensed into dust sized particles that accreted (stuck together as the result of collisions) into protoplanets (Asteroid sized bodies) and then larger planets.
The most accepted model in cosmogony.
states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula
Kant and Laplace proposed the nebular hypothesis over two centuries ago.
Our Solar System formed from a giant, swirling cloud of gas & dust.
The Big Bang Theory is describes a the “all matter and energy once exploded out of a single point”
Electromagnetic force - A force that binds nucleus of an atom.
Protosun - forms in the very center of the accretion disk.
WHY DO SOME SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THAT MARS COULD BE THE FUTURE OF HUMANITY?
Geiod-shaped
Has two major movement:
Rotation –the spinning of the Earth on its axis; causes day and night; starts from East to West
Revolution –occurs as the Earth moves around the Sun
Factors to make a planet habitable:
1.Temperature
Venus -Average temperature: Approximately 471°C (TOO HOT)
Earth -Average temperature: Approximately 14°C(JUST RIGHT)
Mars -Average temperature: Approximately −63 °C (TOO COLD)
The habitable zone corresponds to the range of orbital distance where liquid water can exist on a planet’s surface.
Water
Venus - No water on the surface. Has 0.002% water vapor
Earth - About 71 percent of the Earth's surface is water-covered
Mars - Water still exists in form of polar ice caps.
The presence of water allowed the first photosynthetic organisms to thrive.
Atmosphere
It is a thin layer of gases that hover above our planet's surface, that is held in place by the gravity of that body.
Any planet devoid of an atmosphere would have an average surface temperature below freezing and would experience unpredictable and extreme weather and climates. It would also have an extreme amount of UV radiation because there is no atmosphere that absorbs radiation.
Energy (Heat Energy)
Heat coming from Earth is caused by radiogenic heat from radioactive decay of materials in the core and mantle, and extruded via active tectonic activities, such as volcanism and plate movement.
Heat radiated by the sun is mostly trapped by the atmosphere. This creates the heat needed by organisms on Earth.
Having an atmosphere capable of providing heat like in a greenhouse, the atmosphere is therefore a vital part of photosynthesis.
Earth’s Subsystem
Geosphere
Solid Earth
It is composed of rocks and regolith.
It includes all landforms.
Hydrosphere
It is the totality of Earth’s water
Cryosphere - permanently frozen parts.
Atmosphere
It is the mixture of gases that surrounds a planet
It is composed of 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 0.9% Argon, and 0.10% other gases.
Biosphere
It includes all life forms and even organic matter that has not yet decomposed.


It is the zone where interactions between subsystem is most dynamic.
 Knowt
Knowt
