
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is a technology to gather information and analyzing an object or phenomenon without making any direct contact
Remote sensing satellites are satellites equipped with sensors that observe the earth and collect remote sensing data
Optical and Infrared Remote Sensing uses satellites with optical sensors to detect solar radiation reflected or scattered from the earth and thus develop images of Earth
Why do we use remote sensing?
Automated
Useful for extreme conditions
Offers excellent spatial and temporal coverage
Provides real-time or near-real-time observations
Often cost-effective
Extends our senses
Monitor changes to an environment over time
Remote sensing interpretation and analysis techniques:
Visual interpretation
Radiation (reflectance) analysis
Each pixel has a numeric value representing the amount of energy reflected in specific wavelengths – which can be used to characterize the condition of the object
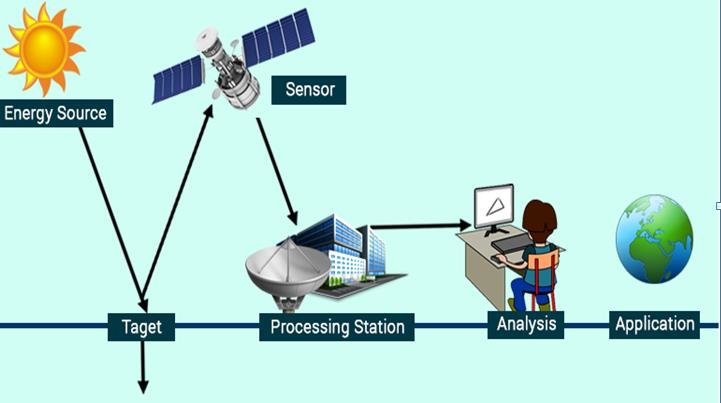
The principles of remote sensing is illustrated in the diagram below:
Electromagnetic Spectrum & Wavelengths in Remote Sensing
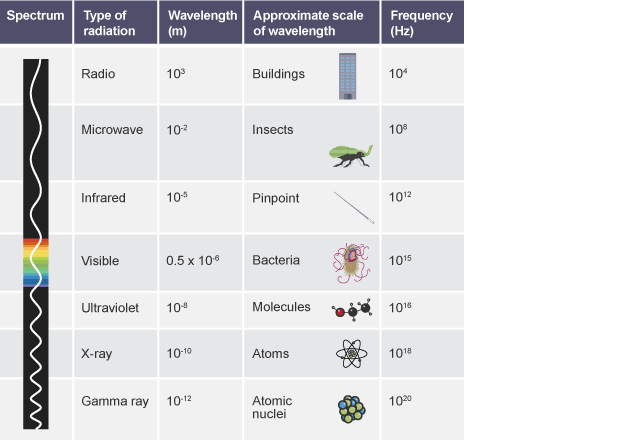
Firstly, below is the electromagenetic spectrum:
Application in GIS
Any remotely sensed parameter, which directly or indirectly characterizes the nature and/or condition of the object under observation, is defined as its signature.
The spectral signatures of an object is defined as the unique pattern of wavelengths radiated by an object
Spectral reflectance characteristics of a healthy green vegetation:
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is a technology to gather information and analyzing an object or phenomenon without making any direct contact
Remote sensing satellites are satellites equipped with sensors that observe the earth and collect remote sensing data
Optical and Infrared Remote Sensing uses satellites with optical sensors to detect solar radiation reflected or scattered from the earth and thus develop images of Earth
Why do we use remote sensing?
Automated
Useful for extreme conditions
Offers excellent spatial and temporal coverage
Provides real-time or near-real-time observations
Often cost-effective
Extends our senses
Monitor changes to an environment over time
Remote sensing interpretation and analysis techniques:
Visual interpretation
Radiation (reflectance) analysis
Each pixel has a numeric value representing the amount of energy reflected in specific wavelengths – which can be used to characterize the condition of the object
The principles of remote sensing is illustrated in the diagram below:

Electromagnetic Spectrum & Wavelengths in Remote Sensing
Firstly, below is the electromagenetic spectrum:

Application in GIS
Any remotely sensed parameter, which directly or indirectly characterizes the nature and/or condition of the object under observation, is defined as its signature.
The spectral signatures of an object is defined as the unique pattern of wavelengths radiated by an object
Spectral reflectance characteristics of a healthy green vegetation:
 Knowt
Knowt