
Chapter 21 - Short-term economic fluctuations
Recessions and expansions
Business cycles: short-term fluctuations in GDP and other variables.
Recession = contraction: period in which the economy is growing at a rate significantly below normal.
Depression: particularly severe or protracted recession.
Peak: beginning of a recession; the high point of economic activity prior to a downturn.
Trough: end of a recession; the low point of economic activity prior to a recovery.
Expansion: period in which the economy is growing at a rate significantly above normal.
Boom: particularly strong and protracted expansion.
Output gaps and cyclical unemployment
Potential output, Y* (or potential GDP or full employment output): maximum sustainable amount of output (real GDP) that an economy can produce.
Output gap: difference between the economy's actual output and its potential output, relative to potential output, at a point in time.
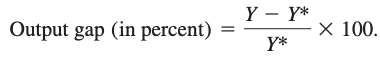
Recessionary gap: negative output gap, which occurs when potential output exceeds actual output (Y < Y*).
Expansionary gap: positive output gap, which occurs when actual output is higher than potential output (Y > Y*).
Natural rate of unemployment, u*: part of the total unemployment rate that is attributable to frictional and structural unemployment; equivalently, the unemployment rate that prevails when cyclical unemployment is zero, so that the economy has neither a recessionary nor an expansionary output gap.
Okun's law: each extra percentage point of cyclical unemployment is associated with about a 2 percent widening of a negative output gap, measured in relation to potential output.
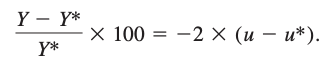
Chapter 21 - Short-term economic fluctuations
Recessions and expansions
Business cycles: short-term fluctuations in GDP and other variables.
Recession = contraction: period in which the economy is growing at a rate significantly below normal.
Depression: particularly severe or protracted recession.
Peak: beginning of a recession; the high point of economic activity prior to a downturn.
Trough: end of a recession; the low point of economic activity prior to a recovery.
Expansion: period in which the economy is growing at a rate significantly above normal.
Boom: particularly strong and protracted expansion.
Output gaps and cyclical unemployment
Potential output, Y* (or potential GDP or full employment output): maximum sustainable amount of output (real GDP) that an economy can produce.
Output gap: difference between the economy's actual output and its potential output, relative to potential output, at a point in time.
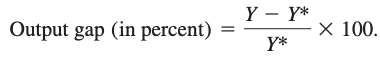
Recessionary gap: negative output gap, which occurs when potential output exceeds actual output (Y < Y*).
Expansionary gap: positive output gap, which occurs when actual output is higher than potential output (Y > Y*).
Natural rate of unemployment, u*: part of the total unemployment rate that is attributable to frictional and structural unemployment; equivalently, the unemployment rate that prevails when cyclical unemployment is zero, so that the economy has neither a recessionary nor an expansionary output gap.
Okun's law: each extra percentage point of cyclical unemployment is associated with about a 2 percent widening of a negative output gap, measured in relation to potential output.
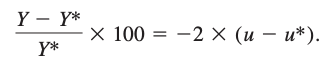
 Knowt
Knowt