
Lab 3: Electroencephalogram
Electroencephalogram (EEG) : recording of electrical activity from cortical neurons of the brain
Correlation between activity level or level of input and synchronization of cortical neurons
Neurons will depolarize as long as individual is alive, regardless of activity or input level
Activity or input level determines depolarization pattern
Increased input → decreased synchronization → increased frequency
Neurons respond and depolarize as sensory input arrives
Decreased input → increased synchronization → decreased frequency
Neurons synchronize and depolarize together
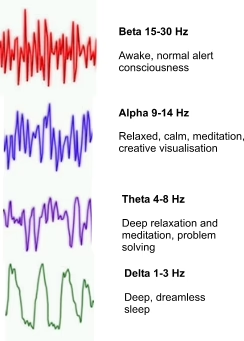
Named wave patterns defined by range of frequency and amplitude
Overall wave pattern named for wave type that dominates
Amplitude and frequency inversely related
Beta: 14-30 Hz, 5-10 μV, active, alert, and focused
Alpha: 8-13 Hz, 8-14 μV, awake but drowsey, not active/not focused, daydreaming
Theta: 4-7 Hz, 100 μV, light sleep
Delta: 0.5-3 Hz, 20-200 μV, deep sleep, unconscious
Sleep
Awake
Transition from Beta to alpha waves (due to cutting off visual input - eyes closed)
Four numbered stages (or three numbered stages depending on source) of slow wave or non-REM (NREM) sleep
Sleep stage 1 (SWS1 or NREM1) – brief transition between awake state and sleep state, transition from alpha to theta waves
Slow eye movement and floating sensation
Sleep stage 2 (SWS2 or NREM2) – Light sleep with theta dominant wave pattern
Sleep spindles only occur in stage 2 as response to stimulus → stay asleep/not wake up (higher average of sleep spindle = better sleep)
Slight decrease in breathing and heart rate
Eyes generally still
Stage 3 and 4 (SWS3 and 4 or NREM3 and 4) - deep sleep, delta wave dominant pattern
Oblivious sleep
Decrease in body temp, breathing, and heart rates
Unconscious shifts in position
Sleepwalking
REM (rapid eye movement) - high frequency beta-like wave pattern
Called paradoxical sleep due to the high frequency pattern
Atonia - paralysis of voluntary muscles (sleep paralysis), only extraocular muscles and diaphragm remain active
Most vivid dreams
Cycle through stages
Early cycles include deep sleep
Later cycles only stage 2 and REM
Cycles “shortcut” as time progress
Lab 3: Electroencephalogram
Electroencephalogram (EEG) : recording of electrical activity from cortical neurons of the brain
Correlation between activity level or level of input and synchronization of cortical neurons
Neurons will depolarize as long as individual is alive, regardless of activity or input level
Activity or input level determines depolarization pattern
Increased input → decreased synchronization → increased frequency
Neurons respond and depolarize as sensory input arrives
Decreased input → increased synchronization → decreased frequency
Neurons synchronize and depolarize together
Named wave patterns defined by range of frequency and amplitude
Overall wave pattern named for wave type that dominates
Amplitude and frequency inversely related
Beta: 14-30 Hz, 5-10 μV, active, alert, and focused
Alpha: 8-13 Hz, 8-14 μV, awake but drowsey, not active/not focused, daydreaming
Theta: 4-7 Hz, 100 μV, light sleep
Delta: 0.5-3 Hz, 20-200 μV, deep sleep, unconscious

Sleep
Awake
Transition from Beta to alpha waves (due to cutting off visual input - eyes closed)
Four numbered stages (or three numbered stages depending on source) of slow wave or non-REM (NREM) sleep
Sleep stage 1 (SWS1 or NREM1) – brief transition between awake state and sleep state, transition from alpha to theta waves
Slow eye movement and floating sensation
Sleep stage 2 (SWS2 or NREM2) – Light sleep with theta dominant wave pattern
Sleep spindles only occur in stage 2 as response to stimulus → stay asleep/not wake up (higher average of sleep spindle = better sleep)
Slight decrease in breathing and heart rate
Eyes generally still
Stage 3 and 4 (SWS3 and 4 or NREM3 and 4) - deep sleep, delta wave dominant pattern
Oblivious sleep
Decrease in body temp, breathing, and heart rates
Unconscious shifts in position
Sleepwalking
REM (rapid eye movement) - high frequency beta-like wave pattern
Called paradoxical sleep due to the high frequency pattern
Atonia - paralysis of voluntary muscles (sleep paralysis), only extraocular muscles and diaphragm remain active
Most vivid dreams
Cycle through stages
Early cycles include deep sleep
Later cycles only stage 2 and REM
Cycles “shortcut” as time progress
 Knowt
Knowt
