
NURS-1001 Understanding the Canadian Healthcare System
NURS- 1001 Understanding the Canadian Healthcare System
Evolution of health care system
Healthcare reform
Indigenous health
European Settlers
5th Century
Infectious diseases
Poor sanitation
Public health laws
British North America Act 1867
Constitution act
Self-governing
Public health
Public policy
When Canada became a self-governing country
Urbanization
Social programs
Childrens aids society (1891)
Red Cross (1896)
Victoria Order Nurses (1897)
Mental Health Association (1918)
Municipality Act 1916
Tax revenue to pay physicians
Before this physician's salary was paid by people
Tommy Douglas
Premiere of Saskatchewan
Gave rise to universal healthcare
Medicare
Hospital Insurance & Diagnostic Services Act (1957)
Medical Care Act (1966)
Federal-provincial Fiscal Arrangements and Establishment Programs Financing Act (1977)
Canada Health Act
“ to protect, promote, and restore the physical and mental well-being of residents of Canada and to facilitate reasonable access to health services without financial or other barriers” (Health Canada, 2011)
Prevent any further billing, and stop the divided between those who can and can't afford healthcare
Covers the costs of services directly related with healthcare
Excludes armed forces, inmates, RCMP

Canada Health Transfer
“The largest major federal transfer to provinces and territories. It provides long-term predictable funding for health care and supports the principles of the Canada Health Act (CHA). The transfer is made on an equal per capita basis, to provide comparable treatments for all Canadians, regardless of where they live.” (Government of Canada, 2011)
Governance of Healthcare
Federal- assist in financing, creating national health promotional
Provincial/Territorial -manages healthcare facilities,
Professional -self-regulating professionals
Canadas Healthcare
Nursing workforce
Universal care
Canada Health Act (5 principles that prevent extra billing)
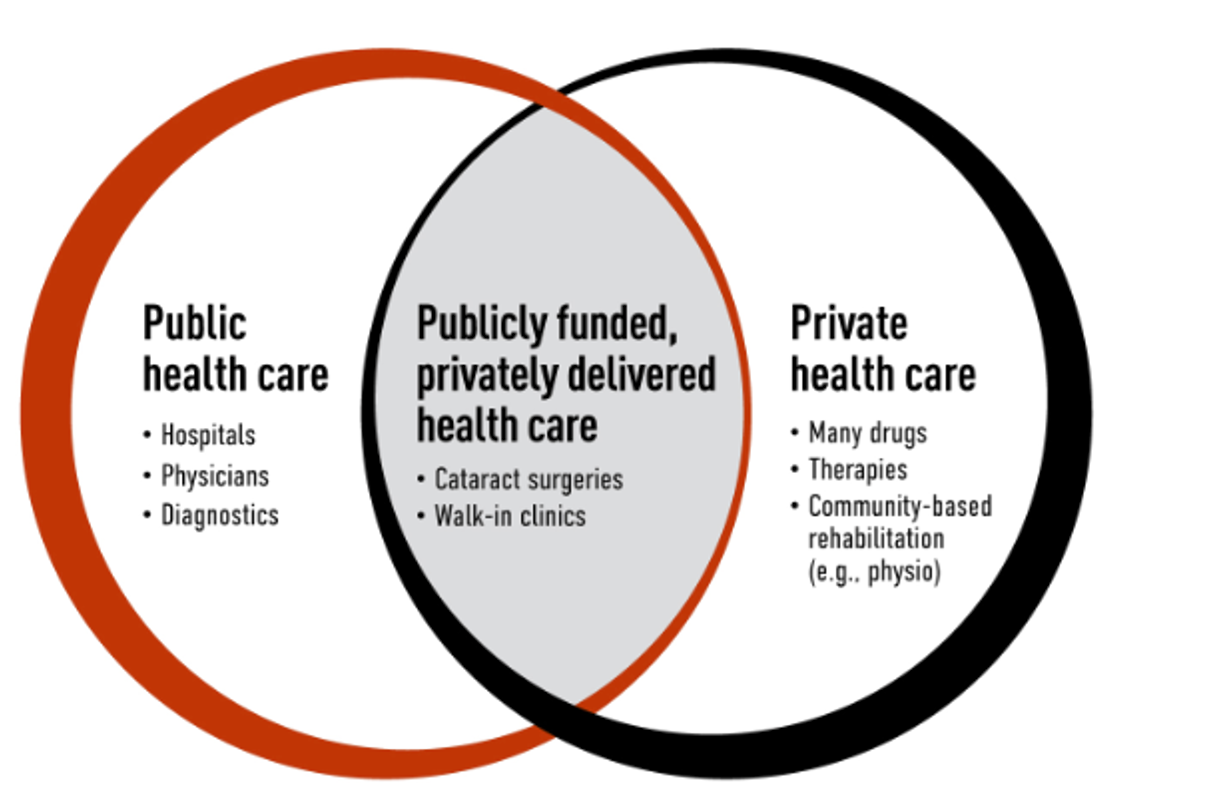
Areas of Care
Primary -Health promotion, mental health promotion (physicians, NP, nurses)
Secondary - specialized care in a hospital, long-term care etc, funding based on budget rather than service. Assessed by medical professional
Tertiary -specialized care for complicated health issues
WHY ARE WE CONCERNED WITH THE PRIVATIZATION OF HEALTHCARE?
Privatization
Staffing
Funding
New regulations
Health inequities
Pressure off the public system?
Wealthier people get better healthcare, best doctors would work here
Ontario Health Coalition
The Power of Peoples Referendum
Activist coalition that is trying to preserve the Canadian healthcare system
Ontario citizens can vote on public or privatization of the healthcare system
Health Care Challenges
Aging population
Chronic disease
Fiscal constraints -Health services becoming expensive (new tech, new drugs, reform)
Access to treatment/wait times -training and training more healthcare professionals
Health Care Reform
Kirby Report (2002) -Assesd problems/solutions with the canadian healthcare system. Recommended gov paying for canadians services even in other ocuntries
Romanow Report (2002) - promoted in primary care, recommended increase funding and changes to the system
10 Year Plan to Strengthen Healthcare (2004)
Future of Health Reform
Patient wait times
Primary Healthcare -Increase the boundaries of practice for physicians (no more doctors only having to practice where they are licensed)
Pharmacare -By funding pharmacare we can prevent future costs of healthcare and deteriorating health
Healthcare Trends
Artificial intelligence -multiple health applications, Ai flag health risks, develop new drugs and treatments, and create strategies for health
Telehealth -remote options
Wearable devices -collects health data that patients and physicians can use, empowers patients to perform healthier habits
Electronic health records -Centralized data in patient reports that allows phsyicans to work together (e.g public health records)
Mental health care -mental health apps, online group therapies, telehealth
Indigenous Health
Infectious diseases
Segregation
Systemic Racism
Treaties
Medicine Chest Clause Treaty 6 (1876)
Indian Act (1876)
Indian Health Policy (1979)
Health Transfer Policy (1989)
Self Governance & Determination
“Self-government negotiations are one way to work together in partnership toward this goal and advance Indigenous rights and principle of international law” (Government of Canada, 2020)
Approach to Implementation of the Inherent Right and the Negotiation of Aboriginal Self-Government (1995)
Joyce Echanquan
37 mother of 7 who died of pulmonary ademia
Came in hospital distruaght and in pain
Staff at hospital did believe her and thought she was going through drug withdrawal
Posted video of her being harassed by hospital satff to facebook
Brain Sinclair
Racism again
Sat in wheelchair for 34 hours before staff relized he died
Thought he was homeless or an alcoholic
Importance of Indigenous Health
Ongoing racism and discrimination
Overcome barriers
Reduce stigma
Smudging
Ceremony involving various plants
The burning of one or more medicines (tobacco, sage, sweetgrass, cedar)
Inhale the smoke
Relevance to Nursing
Complexity of Canadian health care system
Nursing role is evolving
Key stakeholders and policymakers
Summary
Canadas healthcare evolved over time into a universal system. Free of additional charges for hospitalization or primary care
Canada Health Act governs the delivery of heallthcare nationwide, provinces must deliver care based on the 5 principles
Healthcare reform determines changes in policy to improve future of healthcare, major reform for primary care, potential privatization, pharma care
Emerging health trends influence healthcare reform
Indigenous health must be addressed to overcome racism and discrimination
Self-governance gives indigenous communities the power to control policy, economic, political, and cultural affairs within the community
Important for nurses to understand the healthcare system to act as advocates in policy change
Midterm Exam
2 hours
In class
50 multiple choice
25% of final grade
Lecture, reading & seminar content
Knowledge application questions
NURS-1001 Understanding the Canadian Healthcare System
NURS- 1001 Understanding the Canadian Healthcare System
Evolution of health care system
Healthcare reform
Indigenous health
European Settlers
5th Century
Infectious diseases
Poor sanitation
Public health laws
British North America Act 1867
Constitution act
Self-governing
Public health
Public policy
When Canada became a self-governing country
Urbanization
Social programs
Childrens aids society (1891)
Red Cross (1896)
Victoria Order Nurses (1897)
Mental Health Association (1918)
Municipality Act 1916
Tax revenue to pay physicians
Before this physician's salary was paid by people
Tommy Douglas
Premiere of Saskatchewan
Gave rise to universal healthcare
Medicare
Hospital Insurance & Diagnostic Services Act (1957)
Medical Care Act (1966)
Federal-provincial Fiscal Arrangements and Establishment Programs Financing Act (1977)
Canada Health Act
“ to protect, promote, and restore the physical and mental well-being of residents of Canada and to facilitate reasonable access to health services without financial or other barriers” (Health Canada, 2011)
Prevent any further billing, and stop the divided between those who can and can't afford healthcare
Covers the costs of services directly related with healthcare
Excludes armed forces, inmates, RCMP

Canada Health Transfer
“The largest major federal transfer to provinces and territories. It provides long-term predictable funding for health care and supports the principles of the Canada Health Act (CHA). The transfer is made on an equal per capita basis, to provide comparable treatments for all Canadians, regardless of where they live.” (Government of Canada, 2011)
Governance of Healthcare
Federal- assist in financing, creating national health promotional
Provincial/Territorial -manages healthcare facilities,
Professional -self-regulating professionals
Canadas Healthcare
Nursing workforce
Universal care
Canada Health Act (5 principles that prevent extra billing)

Areas of Care
Primary -Health promotion, mental health promotion (physicians, NP, nurses)
Secondary - specialized care in a hospital, long-term care etc, funding based on budget rather than service. Assessed by medical professional
Tertiary -specialized care for complicated health issues
WHY ARE WE CONCERNED WITH THE PRIVATIZATION OF HEALTHCARE?
Privatization
Staffing
Funding
New regulations
Health inequities
Pressure off the public system?
Wealthier people get better healthcare, best doctors would work here
Ontario Health Coalition
The Power of Peoples Referendum
Activist coalition that is trying to preserve the Canadian healthcare system
Ontario citizens can vote on public or privatization of the healthcare system
Health Care Challenges
Aging population
Chronic disease
Fiscal constraints -Health services becoming expensive (new tech, new drugs, reform)
Access to treatment/wait times -training and training more healthcare professionals
Health Care Reform
Kirby Report (2002) -Assesd problems/solutions with the canadian healthcare system. Recommended gov paying for canadians services even in other ocuntries
Romanow Report (2002) - promoted in primary care, recommended increase funding and changes to the system
10 Year Plan to Strengthen Healthcare (2004)
Future of Health Reform
Patient wait times
Primary Healthcare -Increase the boundaries of practice for physicians (no more doctors only having to practice where they are licensed)
Pharmacare -By funding pharmacare we can prevent future costs of healthcare and deteriorating health
Healthcare Trends
Artificial intelligence -multiple health applications, Ai flag health risks, develop new drugs and treatments, and create strategies for health
Telehealth -remote options
Wearable devices -collects health data that patients and physicians can use, empowers patients to perform healthier habits
Electronic health records -Centralized data in patient reports that allows phsyicans to work together (e.g public health records)
Mental health care -mental health apps, online group therapies, telehealth
Indigenous Health
Infectious diseases
Segregation
Systemic Racism
Treaties
Medicine Chest Clause Treaty 6 (1876)
Indian Act (1876)
Indian Health Policy (1979)
Health Transfer Policy (1989)
Self Governance & Determination
“Self-government negotiations are one way to work together in partnership toward this goal and advance Indigenous rights and principle of international law” (Government of Canada, 2020)
Approach to Implementation of the Inherent Right and the Negotiation of Aboriginal Self-Government (1995)
Joyce Echanquan
37 mother of 7 who died of pulmonary ademia
Came in hospital distruaght and in pain
Staff at hospital did believe her and thought she was going through drug withdrawal
Posted video of her being harassed by hospital satff to facebook
Brain Sinclair
Racism again
Sat in wheelchair for 34 hours before staff relized he died
Thought he was homeless or an alcoholic
Importance of Indigenous Health
Ongoing racism and discrimination
Overcome barriers
Reduce stigma
Smudging
Ceremony involving various plants
The burning of one or more medicines (tobacco, sage, sweetgrass, cedar)
Inhale the smoke
Relevance to Nursing
Complexity of Canadian health care system
Nursing role is evolving
Key stakeholders and policymakers
Summary
Canadas healthcare evolved over time into a universal system. Free of additional charges for hospitalization or primary care
Canada Health Act governs the delivery of heallthcare nationwide, provinces must deliver care based on the 5 principles
Healthcare reform determines changes in policy to improve future of healthcare, major reform for primary care, potential privatization, pharma care
Emerging health trends influence healthcare reform
Indigenous health must be addressed to overcome racism and discrimination
Self-governance gives indigenous communities the power to control policy, economic, political, and cultural affairs within the community
Important for nurses to understand the healthcare system to act as advocates in policy change
Midterm Exam
2 hours
In class
50 multiple choice
25% of final grade
Lecture, reading & seminar content
Knowledge application questions
 Knowt
Knowt
