
Buddhism
Buddhism Basics
Originated in India as an offshoot of Hinduism
Believes that the human condition is sick and needs a cure
Gautama Buddha “the enlightened one”
Stories of Buddha’s life were recorded centuries after his death
Born around 560 BCE, died around 480 BCE
Warrior Class; Feudal Lord (very privileged)
Parents made sure he never encountered any suffering
The Four Passing Sights
Left home to see the world in his early 20’s
Parents got rid of slums etc. to ensure that Buddha didn’t see anything that would distress him; didn’t work
Elderly
Disease
Death
Ascetic
Someone who draws away from worldly/physical pleasures to develop spiritually
At age 29, Buddha left the castle and everything he knew
“The [Great] Going Forth”
left to solve old age/disease/death
Attempts to solve old age and death
Solitude
Extreme fasting
Yoga
Comes up with the Middle Way
The Middle Way
Rejection both extremes of life (sensual indulgence and asceticism)
Don’t live excessively or completely ignore your own needs
Spiritual health and physical health are united
Enlightenment
Sat in Lotus position under Bodhi Tree (Wisdom Tree)
Battled Gods, Death, Discontent, Delight, Desire
Each of these tempts him off the path of Enlightenment, so he has to overcome them
Stages of Enlightenment
1: Can see past lives through meditation
2: See death/rebirth of all things
3: The Four Noble Truths are revealed
Temptation
Buddha was tempted to pass into Nirvana but resists
Nirvana: The extinction/letting go of any desires and individual self-worth
Buddha was compassionate and teaching
Described self as “awake”
Buddhism in Practice
Buddha’s Followers
5 people followed him and became saints (arhats)
Founded Sanga
3 Jewels of Buddhism
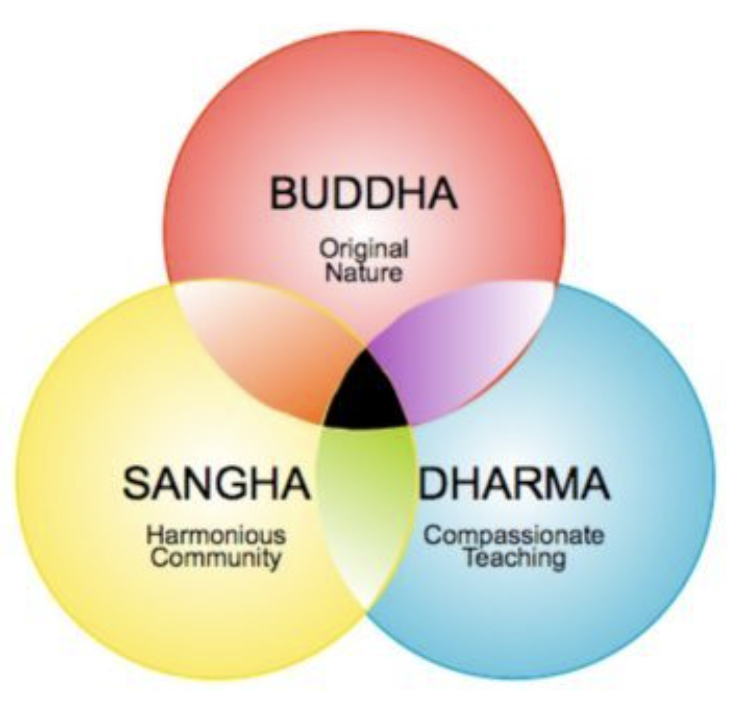
Buddha: Founded Buddhism
Dharma: Teachings of Buddha, how he lived his life
The universe is eternally created and destroyed (Hinduism)
Were many Buddhas before and many will follow
Samsara: The continuous cycle of birth and death
Rejects sacrificial system to the gods/goddesses
Rejects caste system and segmentation of society; allows women to have status
Rejects education (barrier to entry for religion; not accessible for everyone)
Wrote in Pali: the ancient language of common Indians
Center of Dharma wheel = spiritual balance achieved through teachings
Sangha: The community and life of person themself
Destiny
Discover inner realm of self to achieve Nirvana
Everything within and outside of self is changing
Accept that not everything about self is real
Three Marks of Existence
Anatta: There is no self
Opposite of the Hinduism
There is no Atman, Brahman, self, essence, ultimate reality
We don’t have souls, there is only the now
Anicca: Impermanence
Existence is constantly changing
Eg. nature of the river is flowing → you will never step in the same river twice
Dukka: Suffering
Result of other two marks
Suffering exists because people can’t let go/go with the flow → creates suffering for self
Must detach, see everything as loose and changing, don’t try to grasp
Karma
Same in Buddhism and Hinduism
Basic Karma rules of Buddhism:
What is wrong is the intention (why) of a moral act, not the outcome
Four Noble Truths
To live life is to experience dukka
Discomfort, things are not as they should be
The more attachment you have, the more you will suffer
Circumstances in live (chance), stages of growth and development, sickness, old age, all will die, unfulfilled wishes
Suffering is caused by tanha
Tanha: our personal thirsts and desires
Self desire, personal fulfillment — increases dukka and tanha
We are naturally selfish
Suffering can stop
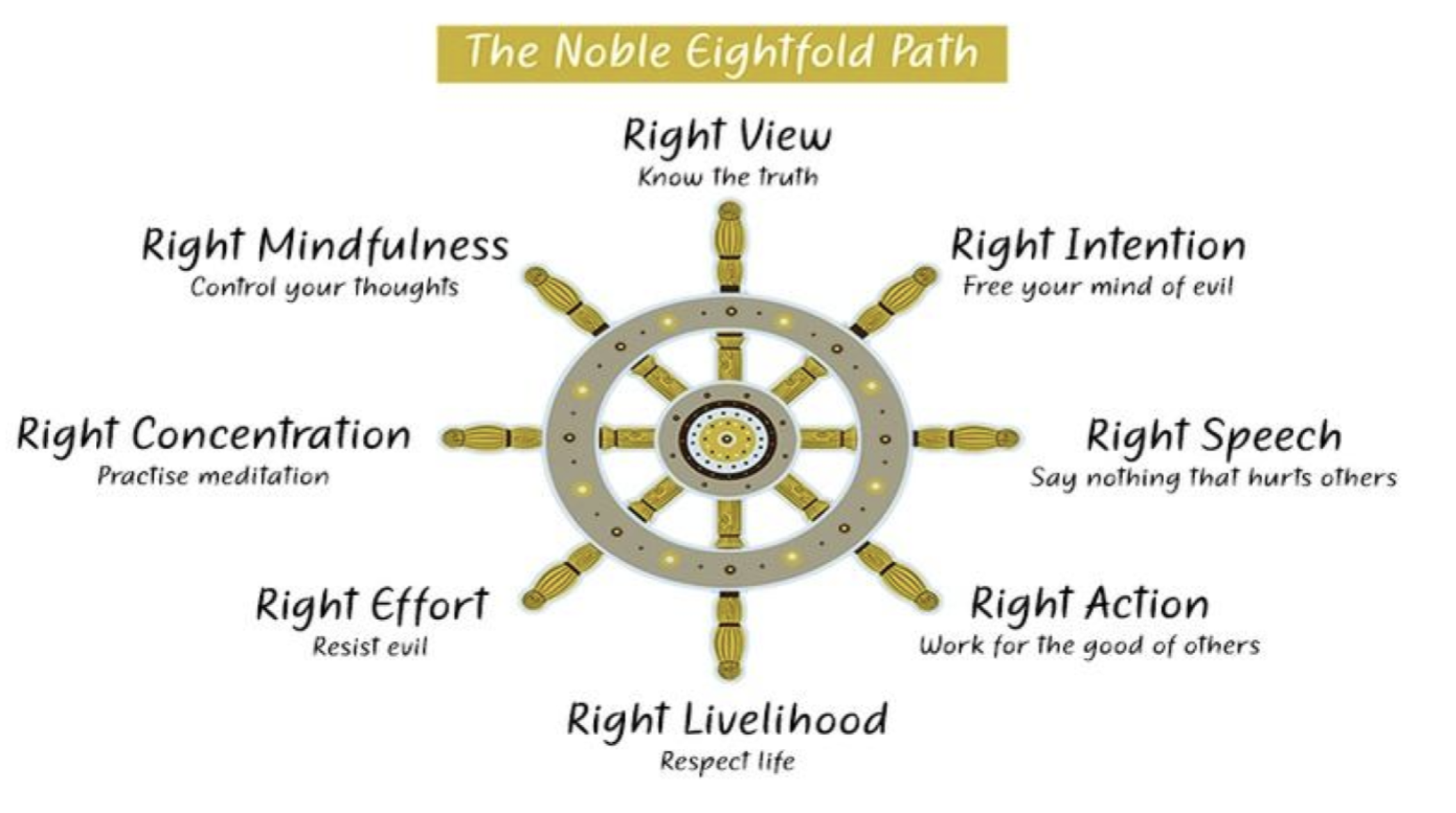
Solution to suffering: the Eightfold Path
The Eightfold Path: The basic practices of Buddhism that can lead you to Nirvana
Enlightenment and Nirvana
Final Nirvana happens at bodily death
Arhat: one who is enlightened/awakened
If you attain it, you see that there is no self, and you are free from tanha and dukka
Buddhas do not need followers or models to attain Nirvana
Nirvana is impossible to describe
Three Ways of Buddhism
Theravada: The Way of the Elders
There are no gods or goddesses to help you
Buddha is the first to experience enlightenment
The teachings of Buddha are the most important thing
Nirvana is attainable by your own effort
Mahayana: The Great Vehicle
Largest sect of Buddhism
See Buddha as a divine savior
Primary teaching: foster compassion
Didn’t enter Nirvana immediately
Goal: become a bodhisatva
Bodhisatva: a Buddha in the making
Can enter Nirvana but stop short to help others
Extend beyond the earthly realm
Wait to enter Nirvana until the last blade of grass becomes enlightened
Vajrayana
Diamond sector teaching of Buddhism - harness
Teachings are full of energy, strength, clarity
Mandala: a pattern of icons/images that visually excite to enhance meditation
Mudras: choreographed hand movements used in ritual
Mantra: a sacred utterance (syllable, word, or verse) that is considered to possess mystical or spiritual efficacy
Rituals are important
Talk with gods/goddesses to achieve union with them and nirvana
Dalai Lama
Spiritual leader of Vajrayana Buddhism
14th reincarnation of bodhisattva
Buddhism
Buddhism Basics
Originated in India as an offshoot of Hinduism
Believes that the human condition is sick and needs a cure
Gautama Buddha “the enlightened one”
Stories of Buddha’s life were recorded centuries after his death
Born around 560 BCE, died around 480 BCE
Warrior Class; Feudal Lord (very privileged)
Parents made sure he never encountered any suffering
The Four Passing Sights
Left home to see the world in his early 20’s
Parents got rid of slums etc. to ensure that Buddha didn’t see anything that would distress him; didn’t work
Elderly
Disease
Death
Ascetic
Someone who draws away from worldly/physical pleasures to develop spiritually
At age 29, Buddha left the castle and everything he knew
“The [Great] Going Forth”
left to solve old age/disease/death
Attempts to solve old age and death
Solitude
Extreme fasting
Yoga
Comes up with the Middle Way
The Middle Way
Rejection both extremes of life (sensual indulgence and asceticism)
Don’t live excessively or completely ignore your own needs
Spiritual health and physical health are united
Enlightenment
Sat in Lotus position under Bodhi Tree (Wisdom Tree)
Battled Gods, Death, Discontent, Delight, Desire
Each of these tempts him off the path of Enlightenment, so he has to overcome them
Stages of Enlightenment
1: Can see past lives through meditation
2: See death/rebirth of all things
3: The Four Noble Truths are revealed
Temptation
Buddha was tempted to pass into Nirvana but resists
Nirvana: The extinction/letting go of any desires and individual self-worth
Buddha was compassionate and teaching
Described self as “awake”
Buddhism in Practice
Buddha’s Followers
5 people followed him and became saints (arhats)
Founded Sanga
3 Jewels of Buddhism

Buddha: Founded Buddhism
Dharma: Teachings of Buddha, how he lived his life
The universe is eternally created and destroyed (Hinduism)
Were many Buddhas before and many will follow
Samsara: The continuous cycle of birth and death
Rejects sacrificial system to the gods/goddesses
Rejects caste system and segmentation of society; allows women to have status
Rejects education (barrier to entry for religion; not accessible for everyone)
Wrote in Pali: the ancient language of common Indians
Center of Dharma wheel = spiritual balance achieved through teachings
Sangha: The community and life of person themself
Destiny
Discover inner realm of self to achieve Nirvana
Everything within and outside of self is changing
Accept that not everything about self is real
Three Marks of Existence
Anatta: There is no self
Opposite of the Hinduism
There is no Atman, Brahman, self, essence, ultimate reality
We don’t have souls, there is only the now
Anicca: Impermanence
Existence is constantly changing
Eg. nature of the river is flowing → you will never step in the same river twice
Dukka: Suffering
Result of other two marks
Suffering exists because people can’t let go/go with the flow → creates suffering for self
Must detach, see everything as loose and changing, don’t try to grasp
Karma
Same in Buddhism and Hinduism
Basic Karma rules of Buddhism:
What is wrong is the intention (why) of a moral act, not the outcome
Four Noble Truths
To live life is to experience dukka
Discomfort, things are not as they should be
The more attachment you have, the more you will suffer
Circumstances in live (chance), stages of growth and development, sickness, old age, all will die, unfulfilled wishes
Suffering is caused by tanha
Tanha: our personal thirsts and desires
Self desire, personal fulfillment — increases dukka and tanha
We are naturally selfish
Suffering can stop
Solution to suffering: the Eightfold Path
The Eightfold Path: The basic practices of Buddhism that can lead you to Nirvana

Enlightenment and Nirvana
Final Nirvana happens at bodily death
Arhat: one who is enlightened/awakened
If you attain it, you see that there is no self, and you are free from tanha and dukka
Buddhas do not need followers or models to attain Nirvana
Nirvana is impossible to describe
Three Ways of Buddhism
Theravada: The Way of the Elders
There are no gods or goddesses to help you
Buddha is the first to experience enlightenment
The teachings of Buddha are the most important thing
Nirvana is attainable by your own effort
Mahayana: The Great Vehicle
Largest sect of Buddhism
See Buddha as a divine savior
Primary teaching: foster compassion
Didn’t enter Nirvana immediately
Goal: become a bodhisatva
Bodhisatva: a Buddha in the making
Can enter Nirvana but stop short to help others
Extend beyond the earthly realm
Wait to enter Nirvana until the last blade of grass becomes enlightened
Vajrayana
Diamond sector teaching of Buddhism - harness
Teachings are full of energy, strength, clarity
Mandala: a pattern of icons/images that visually excite to enhance meditation
Mudras: choreographed hand movements used in ritual
Mantra: a sacred utterance (syllable, word, or verse) that is considered to possess mystical or spiritual efficacy
Rituals are important
Talk with gods/goddesses to achieve union with them and nirvana
Dalai Lama
Spiritual leader of Vajrayana Buddhism
14th reincarnation of bodhisattva
 Knowt
Knowt