
Ch 25 - Economic Integration
Economic Integration: a process whereby countries coordinate and link their economic policies
As economic integration increases, trade barriers increase, monetary/fiscal policies are harmonised
Preferential trade agreements: give preferential access to certain products by reducing or eliminating tariffs, or by other agreements related to trade
Two types:
Bilateral agreements: between two countries → easier to implement
Multilateral agreements: between two or more countries → beneficial to more people
Trading bloc: an agreement where trade barriers ar reduced or eliminated among participating members
Trade bloc advantages:
Free trade within the bloc
Easier access to other market
Firms can expand
More employment due to growth in exports
Trade creation
Trade bloc disadvantages:
Trade diversion
Reduced benefits of free trade
Inefficiencies
Common external tariffs may cause others to retaliate
Trade creation: occurs when the entry of a country into a custom union leads to the production of a good or service transforming from a high-cost producer to a low-cost producer
Beneficial since cheaper supplies from abroad allows for lower prices that benefit the consumer
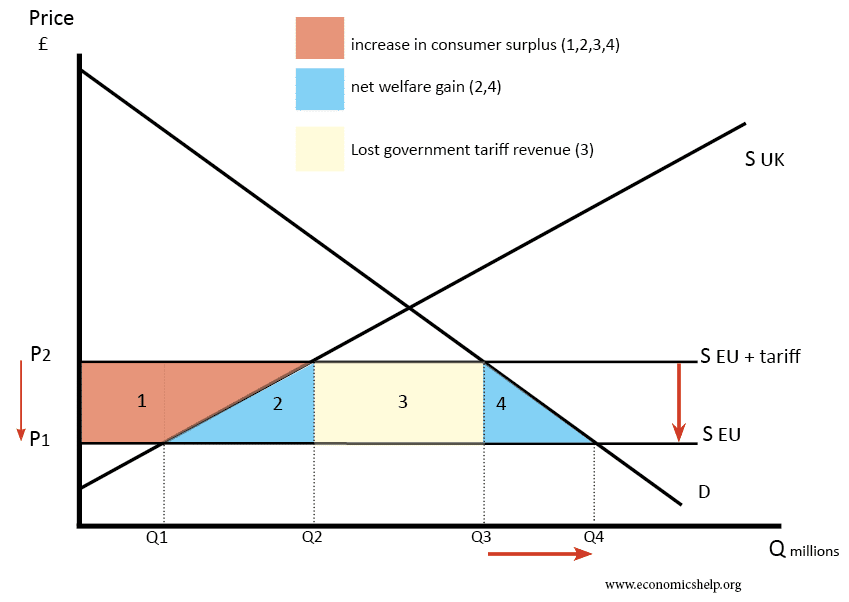
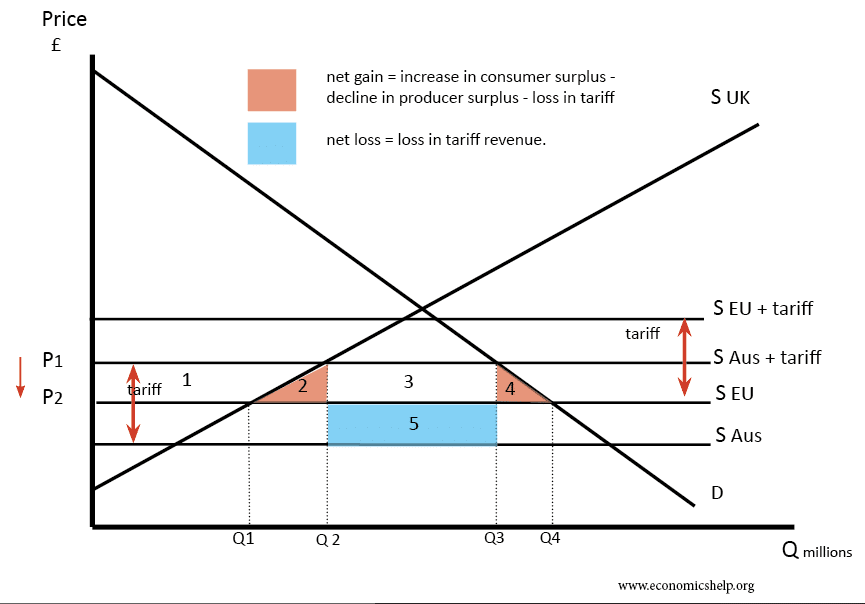
Trade diversion: when the entry of a country into a customs union leads to the protection of a good or service
Trade is diverted from a more efficient exporter to a less efficient one, rather than creating new trade. Due to the common external tariff that the country agrees to.
May not be the best at promoting free trade
Monetary union: agreement between two or more countries creating a single currency
Monetary union advantages:
Transparency: International price of goods can be easily compared
lower transaction costs: single currency, no need to change currency
certainty: price changes are more predictable
better for the job market as it leads to more employment
Monetary union disadvantages:
Loss of economic sovereignty: individual countries cannot set their own interest rates
Inefficiencies firms within the union are favoured more over efficient firms outside the union
Ch 25 - Economic Integration
Economic Integration: a process whereby countries coordinate and link their economic policies
As economic integration increases, trade barriers increase, monetary/fiscal policies are harmonised
Preferential trade agreements: give preferential access to certain products by reducing or eliminating tariffs, or by other agreements related to trade
Two types:
Bilateral agreements: between two countries → easier to implement
Multilateral agreements: between two or more countries → beneficial to more people
Trading bloc: an agreement where trade barriers ar reduced or eliminated among participating members
Trade bloc advantages:
Free trade within the bloc
Easier access to other market
Firms can expand
More employment due to growth in exports
Trade creation
Trade bloc disadvantages:
Trade diversion
Reduced benefits of free trade
Inefficiencies
Common external tariffs may cause others to retaliate
Trade creation: occurs when the entry of a country into a custom union leads to the production of a good or service transforming from a high-cost producer to a low-cost producer
Beneficial since cheaper supplies from abroad allows for lower prices that benefit the consumer

Trade diversion: when the entry of a country into a customs union leads to the protection of a good or service
Trade is diverted from a more efficient exporter to a less efficient one, rather than creating new trade. Due to the common external tariff that the country agrees to.
May not be the best at promoting free trade

Monetary union: agreement between two or more countries creating a single currency
Monetary union advantages:
Transparency: International price of goods can be easily compared
lower transaction costs: single currency, no need to change currency
certainty: price changes are more predictable
better for the job market as it leads to more employment
Monetary union disadvantages:
Loss of economic sovereignty: individual countries cannot set their own interest rates
Inefficiencies firms within the union are favoured more over efficient firms outside the union
 Knowt
Knowt
