
Rhetorical Situation & Argumentation
BIG IDEA #1: The Rhetorical Situation
Speaker- who is talking (sometimes the author)
Audience- who the speaker is addressing
Message- the main point
Tone- the attitude of the speaker toward the message
Persona- the relationship between the speaker and the audience
Medium- how the medium gets there (movie, book, poem, etc)
Diction- words (+ or -) (high or low)
Syntax- order of words
Figurative Language- deep-meaning sayings
Allusion- historical parallels
Irony- opposite
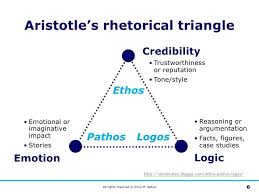
Ethos- trustworthiness of the speaker
Pathos- self-interest
Logos- the principle on what it’s based on (ex God)
Kairos- historical situation/context
Exigence- what’s sticking in the speaker’s craw
Purpose- what the author is trying to do for the audience
Rhetorical Triangle:
BIG IDEA #2: Argumentation
Syllogisms- an instance of a form of reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn (whether validly or not) from two given or assumed propositions (premises), each of which shares a term with the conclusion, and shares a common or middle term not present in the conclusion
All Ducks are Birds
All Birds are animals
All Ducks are animals
Toulmin Model:

Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning:
Deductive- information → claim
Inductive- claim → information
Rhetorical Situation & Argumentation
BIG IDEA #1: The Rhetorical Situation
Speaker- who is talking (sometimes the author)
Audience- who the speaker is addressing
Message- the main point
Tone- the attitude of the speaker toward the message
Persona- the relationship between the speaker and the audience
Medium- how the medium gets there (movie, book, poem, etc)
Diction- words (+ or -) (high or low)
Syntax- order of words
Figurative Language- deep-meaning sayings
Allusion- historical parallels
Irony- opposite
Ethos- trustworthiness of the speaker
Pathos- self-interest
Logos- the principle on what it’s based on (ex God)
Kairos- historical situation/context
Exigence- what’s sticking in the speaker’s craw
Purpose- what the author is trying to do for the audience
Rhetorical Triangle:

BIG IDEA #2: Argumentation
Syllogisms- an instance of a form of reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn (whether validly or not) from two given or assumed propositions (premises), each of which shares a term with the conclusion, and shares a common or middle term not present in the conclusion
All Ducks are Birds
All Birds are animals
All Ducks are animals
Toulmin Model:

Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning:
Deductive- information → claim
Inductive- claim → information
 Knowt
Knowt
